ISG Reporter HEK 293 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ ISG Cells Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-Inducible SEAP Reporter HEK293 Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-isg-1
|
|
||
|
HEK-Blue™ ISG vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-isg-1-av
|
Notification:
Reference #hkb-isg-1-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-isg-1.
Interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-inducible SEAP reporter HEK293 cells
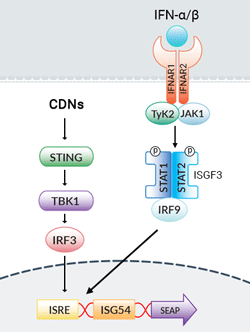
HEK-Blue™ ISG Cells signaling pathway
HEK-Blue™ ISG cells were specifically designed to study the activation of the STING/TBK1/IRF3 signaling pathway by cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs).
CDNs in the cytosol bind directly to STING leading to TBK1-mediated IRF3 activation and type I interferon (IFN) production [1]. IFNs activate the JAK-STAT pathway with the subsequent activation of IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) in the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG).
Cell line description:
HEK-Blue™ ISG cells were derived from the PEAKrapid cell line (similar to ATCC® CRL-2828™) which itself was derived from the human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cell line.
HEK-Blue™ ISG cells express a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) under the control of the IRF-inducible promoter comprised of five IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) fused to an ISG54 minimal promoter.
The presence of CDNs in the cytosol of HEK-Blue™ ISG cells will induce the production of the IRF-inducible SEAP reporter directly by activating the STING/TBK1/IRF3 pathway and indirectly through the activation of the JAK/STAT/IRF9 pathway with type I IFN.
Levels of SEAP in the supernatant can be easily determined with QUANTI- Blue™ Solution, a reagent that turns purple/blue in the presence of SEAP and by reading the OD at 620-655 nm.
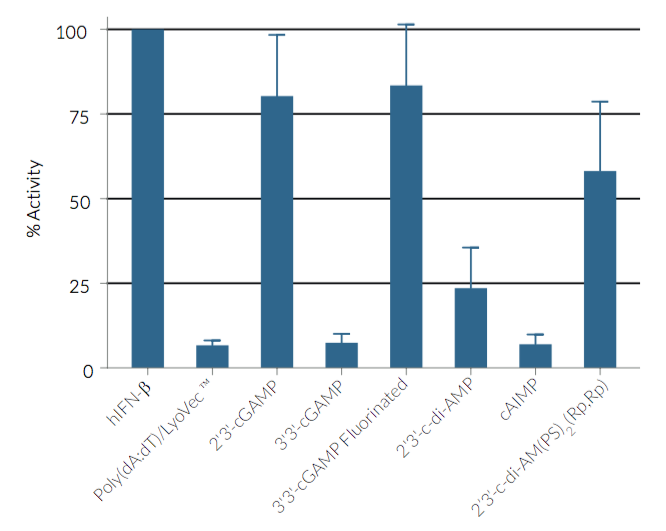
HEK-Blue™ ISG cells respond strongly to non-canonical CDNs, namely 2’3’-cGAMP but poorly to cytosolic DNA, DMXAA, and canonical CDNs.
Features of HEK-Blue™ ISG cells:
- Fully functional STING/TBK1/IRF signaling pathway
- Readily assessable SEAP reporter activity
- Functionally tested and guaranteed mycoplasma-free
Application of HEK-Blue™ ISG cells:
- Studying the STING/TBK1/IRF signaling pathway
Reference:
1. Wan D. et al., 2020. Research Advances in How the cGAS-STING Pathway Controls the Cellular Inflammatory Response. Front Immunol. 11:615.
Back to the topSpecifications
Antibiotic resistance: G418, Zeocin®
Growth Medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), Pen-Strep (100 U/ml - 100 µg/ml), 100 µg/ml Normocin™, 2 mM L-glutamine
Test Medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated FBS (30 min at 56°C), Pen-Strep (100 U/ml - 100 µg/ml), 100 µg/ml Normocin™, 2 mM L-glutamine
Quality control:
- Reporter activity is validated upon stimulation with IFN-α or IFN-β and IRF3 activators.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
- 1 ml Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent).
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
STING (stimulator of interferon genes; also known as TMEM173, MITA, MPYS and ERIS) is essential for the interferon (IFN) response to cytosolic nucleic acids, such as microbial or self-DNA [1, 2], and acts as a direct sensor of cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) [3]. CDNs are important second messenger molecules in bacteria, affecting numerous responses of the prokaryotic cell. In mammalian cells, CDNs act as agonists of the innate immune response [4]. CDNs bind directly to and activate STING leading to TANK Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1)-dependent interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) activation and type I IFN production. IFNs then activate the JAK-STAT pathway with subsequent activation of IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) in the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG).
1. Wan D. et al., 2020. Research Advances in How the cGAS-STING Pathway Controls the Cellular Inflammatory Response. Front Immunol. 11:615.
2. Ishikawa H. & Barber, G., 2008. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455, 674–678.
3. Burdette D.L. et al., 2011. STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP. Nature 478(7370):515-8.
4. Wu J. et al., 2013. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science 339(6121):826-30.