TLR4 agonist preparation - MPLA-SM
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MPLA-SM Monophosphoryl Lipid A from S. minnesota R595 |
Show product |
1 mg |
tlrl-mpla
|
|
Monophosphoryl Lipid A from Salmonella minnesota R595 – Natural preparation
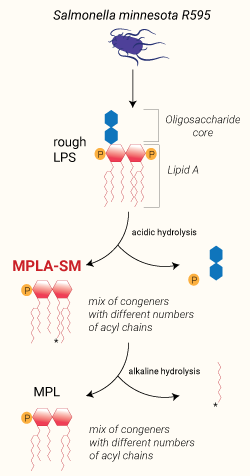
Principle of MPLA-SM extraction
(click to enlarge)
MPLA-SM is a research-grade preparation of Monophosphoryl Lipid A (MPLA) for Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) activation. It is derived from the lipopolysaccharide (LPS, aka endotoxin) of Salmonella minnesota R595 (Re mutant), a rough strain of Gram-negative bacteria.
MPLA-SM is extracted from LPS using treatment with acid and heat followed by chromatography [1]. This preparation contains a mix of MPLA congeneric forms differing in the number of acyl chains. This congener mix is responsible for the partial TLR4 agonist function of some preparations [2].
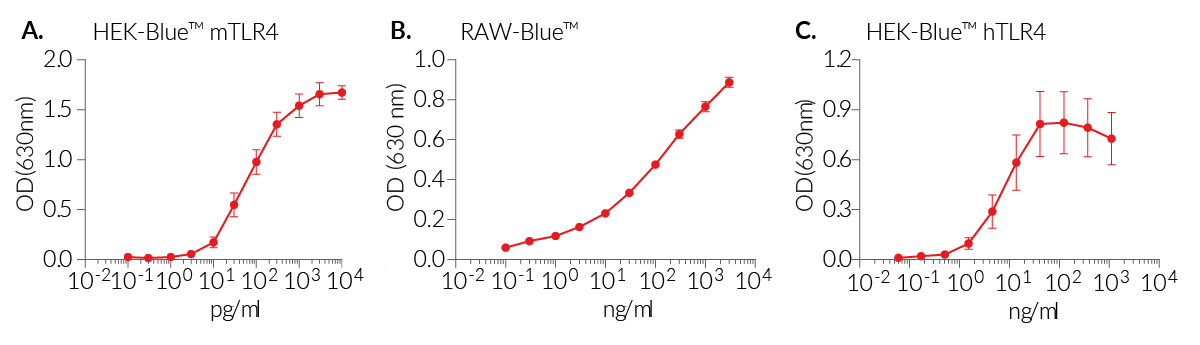
MPLA-SM is a potent activator of TLR4 and does not activate TLR2 or other TLRs. All lots of MLPA-SM display the same ability to activate murine TLR4 but some lots are more potent than others at inducing human TLR4 responses (see figures).
Note: MPLA-SM lots that display a higher potency for human TLR4 are denoted with an asterisk (MPLA-SM*, cat code tlrl-mpla2).
Application
MPLA-SM is a detoxified derivative of lipid A, the biological active component of LPS. Thus MPLA-SM features the immunostimulatory effects of LPS without the adverse effects of the native endotoxin [3]. MPLA-SM, as well as other detoxified derivatives of lipid A, including synthetic hexa-acylated MPLA and 3-O-desacyl-4’-monophosphoryl lipid A (also known as MPL), are used as adjuvants in vaccination studies. MPL® is a clinical grade vaccine adjuvant that is manufactured exclusively by GlaxoSmithKIine [1].
Key features
- Agonist of mouse and human TLR4
- Enhanced activity towards human TLR4 (for MPLA-SM*)
- Negligible TLR2 activity
-
Each lot is functionally tested
Note: MPLA-SM is also available in a pre-clinical grade as MPLA-SM VacciGrade™.
References:
1. Wang YQ. et al., 2020. MPL Adjuvant Contains Competitive Antagonists of Human TLR4. Front. Immunol. 11:577823.
2. Kuzmich, NN. et al., 2017. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. Vaccines (Basel) 5unol. 165(2):618-22.
3. Sarkar, I. et al., 2019. Selection of adjuvants for vaccines targeting specific pathogens. Expert Rev Vaccines. 18(5):505-521.
Specifications
Species: Salmonella enterica serovar minnesota mutant R595
Specificity: TLR4 agonist
Working concentration: 3 ng - 1 μg/ml (for HEK-Blue™ hTLR4 cells) and 10 pg - 100 ng/ml (for HEK-Blue™ mTLR4 cells)
Appearance: Clear lipidic film
Solubility: 1 mg/ml in DMSO
Quality control:
-
Biological activity is validated using cellular assays.
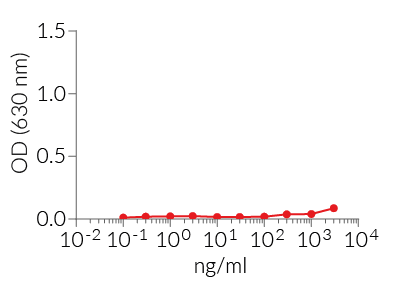
Note: MPLA-SM lots that display a higher potency for human TLR4 are denoted with an asterisk (MPLA-SM*, cat code tlrl-mpla2). - The absence of other bacterial components (e.g. lipoproteins) is controlled using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 cells.
Back to the top
Contents
MPLA-SM is provided as a clear, lyophilized lipidic film.
Note: MPLA-SM lots that display a higher potency for human TLR4 are denoted with an asterisk (MPLA-SM*, cat code tlrl-mpla2).
- 1 mg Monophosphoryl Lipid A (MPLA-SM)
![]() The product is shipped at room temperature.
The product is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Store at -20°C. Upon resuspension, prepare aliquots and store them at -20°C.
Store at -20°C. Upon resuspension, prepare aliquots and store them at -20°C.
![]() The product is stable for 6 months at -20°C.
The product is stable for 6 months at -20°C.
![]() Avoid repeated free
Avoid repeated free
Details
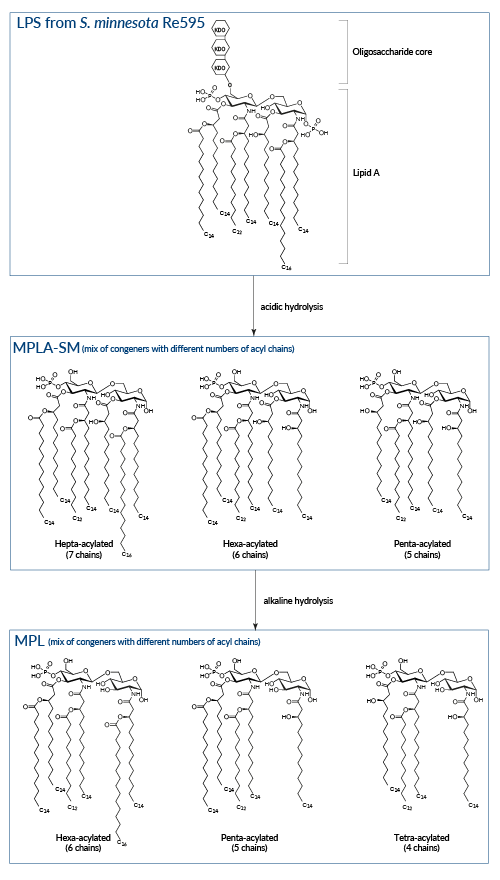
Sequential hydrolysis of LPS from Salmonella minnesota
(click to enlarge)
LPS is a potent activator of TLR4, triggering both NF-κB and IRF-mediated production of pro-inflammatory cyokines and interferons [2]. Thus, LPS features many characteristics needed for an effective vaccine adjuvant. However, large uncontrolled amounts of LPS are extremely toxic and can cause devastating diseases [3]. This led to investigations to define, extract, or synthesize the immunologically active portion of LPS with the lowest toxicity, such as MPLA-SM and MPL®.
LPS
Wild-type LPS, referred to as smooth (sLPS) comprises three covalently linked regions: a Lipid A backbone, a core carbohydrate group, and O-polysaccharide chains. Some bacteria, such as Salmonella minnesota R595, produce a truncated LPS, without O-side chains, referred to as rough (rLPS) [4].
Lipid A
LPS biological activity is mediated by Lipid A recognition by TLR4 and is commensurate to the number of Lipid A fatty acyl chains [3]. Hexa-acylated (6 chains) Lipid A is a highly potent TLR4 agonist, while under‑acylated (4-5 chains) Lipid A induces lower or antagonistic responses [5].
MPLA-SM
The removal of the core carbohydrate group and one phosphate group from the glucosamine disaccharide by acidic treatement of LPS produces MPLA. This derivative displays reduced toxicity while retaining the ability to activate TLR4 [6, 7]. It has been suggested that the reduced toxicity of MPLA is attributed to the preferential triggering of the IRF pathway upon TLR4 activation, resulting in decreased induction of inflammatory cytokines [8]. InvivoGen's MPLA-SM is a research-grade MPLA extracted from LPS of S. minnesota.
MPL
An additional base hydrolysis of MPLA removes one specific fatty acid and generates 3-O-deacylated monophosphoryl lipid A (also known as MPL, 3D-MPL, or 3D-MLA). This deacylation step further decreases the compound residual toxicity. MPL® is a clinical grade vaccine adjuvant that is manufactured exclusively by GlaxoSmithKIine [1].
1. Wang YQ. et al., 2020. MPL Adjuvant Contains Competitive Antagonists of Human TLR4. Front. Immunol. 11:577823.
2. Kuzmich, NN. et al., 2017. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. Vaccines (Basel) 5unol. 165(2):618-22.
3. Steimle, A. et al., 2016. Structure and function: Lipid A modifications in commensals and pathogens. Int J Med Microbiol 306, 290-301.
4. Raetz CR. 1990. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 129‑70.
5. Cochet, F. & Peri, F. 2017. The role of carbohydrates in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Signalling. Int J Mol Sci 18.
6. Qureshi N. et al., 1985. Monophosphoryl lipid A obtained from lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota R595. Purification of the dimethyl derivative by high-performance liquid chromatography and complete structural determination. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 5271–8.
7. Romero CD. et al., 2011. The Toll-Like Receptor 4 agonist monophosphoryl Lipid A augments innate host resistance to systemic bacterial infection. Infect Immun. 79: 3576–3587.
8. Mata-Haro V. et al., 2007. The vaccine adjuvant monophosphoryl lipid A as a TRIF-biased agonist of TLR4. Science. 316(5831):1628-32.