pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3 Plasmid encoding murine IgG1e3 heavy chain constant region |
Show product |
20 µg |
pfuse-mchg1e3
|
|
||
|
pFUSEss-CHIg-mG1e3 Plasmid encoding murine IgG1e3 heavy chain constant region with the IL-2 signal sequence |
Show product |
20 µg |
pfusess-mchg1e3
|
|
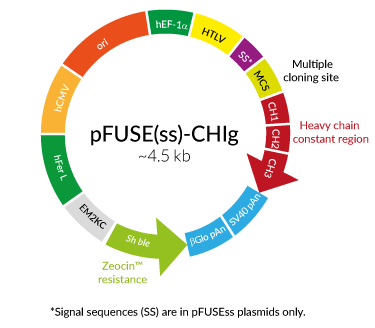
pFUSE-CHIg general plasmid map
Effectorless murine IgG1 heavy chain constant region
pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3 is a cloning plasmid that encodes the constant region of the heavy chain (CH) for a murine IgG1 (mIgG1) that is devoid of effector function and has increased affinity for Protein A.
This engineered mIgG1 contains two point mutations: D265A (a replacement of aspartic acid by alanine at position 265) and T252M (a replacement of threonine with methionine at position 252). The D265A mutation results in a complete loss of cytolytic effector function [1], while the T252M mutation increases affinity for Protein A and enables efficient purification by affinity chromatography [2].
Key features of pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3
- Encodes the effectorless mIgG1e3 CH constant region (D265A + T252 mutations)
- Long-lasting expression due to the composite hEF1-HTLV promoter
- Selectable with Zeocin™ in both bacterial and mammalian cells
- Available with or without the IL-2 signal sequence
This plasmid is designed for recombinant antibody generation. Upstream of the constant region is a unique multiple cloning site (MCS) that enables the insertion of the CH variable region of any given monoclonal antibody (mAb). For the expression of the effectorless mIgG1e3 mAb with the desired antigen affinity, both the pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3 and pFUSE-CLIg (containing the relevant light chain variable region) plasmids must be co-transfected into mammalian cells.
pFUSEss-CHIg-mG1e3 additionally features the human interleukin-2 (IL-2) signal sequence to allow the secretion of recombinant antibodies generated using fragment antigen-binding (Fab) or single-chain variable fragment (scFv) fragments selected from phage display libraries that lack a signal sequence.
References:
1. Baudino L. et al., 2008. Crucial role of aspartic acid at position 265 in the CH2 domain for murine IgG2a and IgG2b Fc-associated effector functions. J Immunol. 181(9):6664-9.
2. Nagaoka M. & Akaike T., 2003. Single amino acid substitution in the mouse IgG1 Fc region induces drastic enhancement of the affinity to protein A. Protein Eng. 16(4):243-5.
Specifications
pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3 & pFUSEss-CHIg-mG1e3:
- Heavy chain constant region: Murine IgG1e3 (contains D265A & T252M point mutations)
- Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin™ (selectable in both bacterial and mammalian cells)
pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3:
- No signal sequence on plasmid
- Cloning sites: 5’- AgeI, EcoRI, EcoRV, XhoI, NheI, and Eco47III -3’
pFUSEss-CHIg-mG1e3:
- Signal sequence: Human interleukin-2 (IL-2)
- Cloning sites: 5’- EcoRI, EcoRV, XhoI, NheI, and Eco47III -3’
Quality control:
- Plasmid construct has been confirmed using DNA sequencing and restriction analysis
- Purified by ion-exchange chromatography
Contents
- 20 µg of lyophilized plasmid DNA
- 1 ml of Zeocin™ (100 mg/ml)
![]() Product is shipped at room temperature.
Product is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, the product should be stored at -20°C.
Upon receipt, the product should be stored at -20°C.
![]() Resuspended DNA should be stored at -20°C and is stable for at least 1 year.
Resuspended DNA should be stored at -20°C and is stable for at least 1 year.
Details
Plasmid features of pFUSE-CHIg-mG1e3 & pFUSEss-CHIg-mG1e3
- hEF1-HTLV prom is a composite promoter comprising the Elongation Factor-1α (EF-1α) core promoter and the R segment and part of the U5 sequence (R-U5’) of the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus (HTLV) Type 1 Long Terminal Repeat. The EF-1α promoter exhibits a strong activity and yields a long-lasting expression of a transgene in vivo. The R-U5’ has been coupled to the EF-1α core promoter to enhance the stability of RNA.
- MCS: To facilitate the cloning of the variable heavy (VH) chain, the multiple cloning site contains the following restriction sites that are compatible with many different enzymes.
- SV40 pAn: the Simian Virus 40 late polyadenylation signal enables efficient cleavage and polyadenylation reactions resulting in high levels of steady-state mRNA.
- ori: A minimal E. coli origin of replication to limit vector size, but with the same activity as the longer Ori.
- CMV enh/hFerL prom is a composite promoter combining the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene 1 enhancer and the core promoter of the human ferritin light chain gene. This ubiquitous promoter drives the expression of the Zeocin™-resistance gene in mammalian cells.
-
EM2KC is a bacterial promoter that enables the constitutive expression of the antibiotic resistance gene in E. coli. EM2KC is located within an intron and is spliced out in mammalian cells.
-
βGlo pAn: The human beta-globin 3’UTR and polyadenylation sequence allow the efficient arrest of the transgene transcription.
-
Murine IgG1e3 (Engineered IgG1 heavy chain constant region): When cloning your VH chain region of choice in the MCS, care must be taken to insert the gene in-frame and to preserve the integrity of the heavy chain constant region. The effectorless mIgG1e3 sequence contains two point mutations, D265A (a replacement of aspartic acid by alanine at position 265) and T252M (a replacement of threonine with methionine at position 252). The D265A mutation results in the complete loss of cytolytic effector function. The T252M mutation results in increased affinity for Protein A and enabling efficient purification by affinity chromatography.
-
Zeo: Resistance to Zeocin™ is conferred by the Sh ble gene from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus. The same resistance gene confers selection in both mammalian cells and E. coli.
Signal sequence on pFUSEss-CHIg-mG1e3
-
IL-2ss: The human interleukin-2 (IL-2) signal sequence contains 20 amino acids (MYRMQLLSCIALSLALVTNS) and shares common characteristics with signal peptides of other secretory proteins. The intracellular cleavage of the IL-2 signal peptide occurs after Ser20 and leads to the secretion of the immunoglobulin chain.




