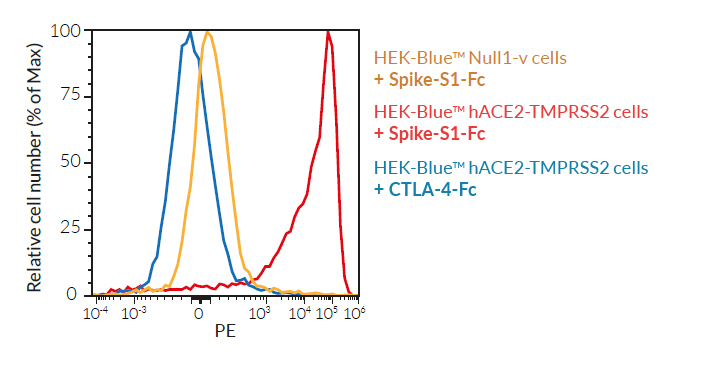
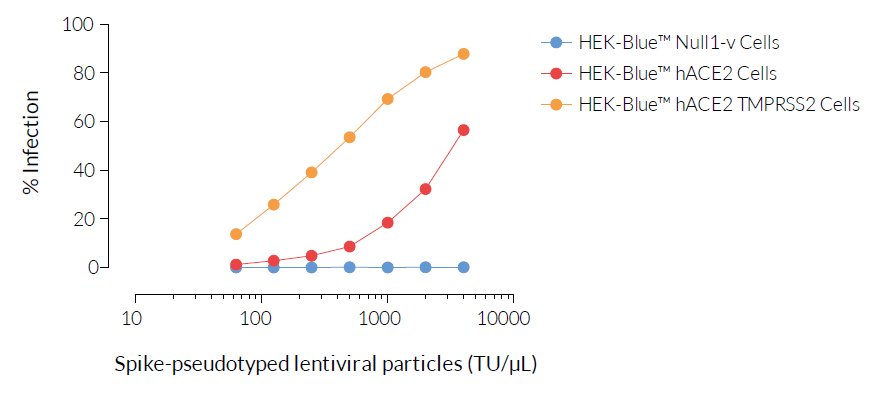
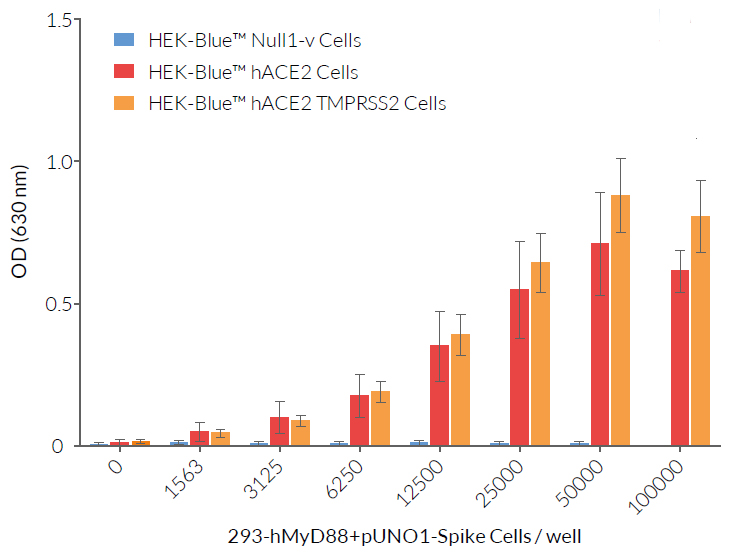
ACE2 expressing HEK293 cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ hACE2 Cells SEAP reporter HEK293 cells expressing human ACE2 |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-hace2
|
|
||
|
HEK-Blue™ hACE2 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-hace2-av
|
|||
|
HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 Cells SEAP reporter HEK293 cells expressing human ACE2 and TMPRSS2a |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-hace2tpsa
|
|
||
|
HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-hace2tpsa-av
|
Notification: Reference #hkb-hace2-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-hace2.
Reference #hkb-hace2tpsa-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-hace2tpsa.
HEK293 NF-κB-reporter cells expressing the SARS-CoV-2 receptors
InvivoGen offers human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK-293)-derived cell lines, specifically designed for COVID-19 studies:
— HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 cells
— HEK-Blue™ hACE2 cells
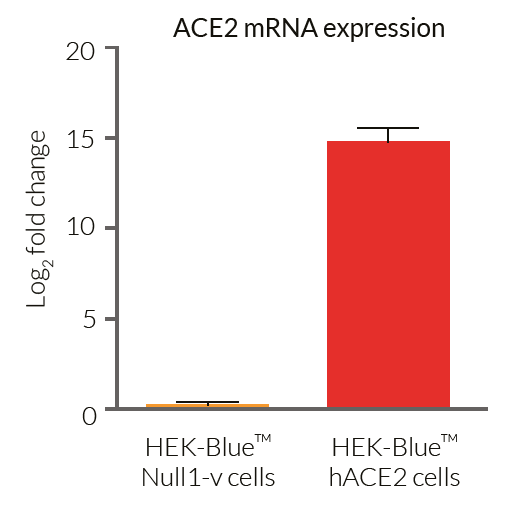
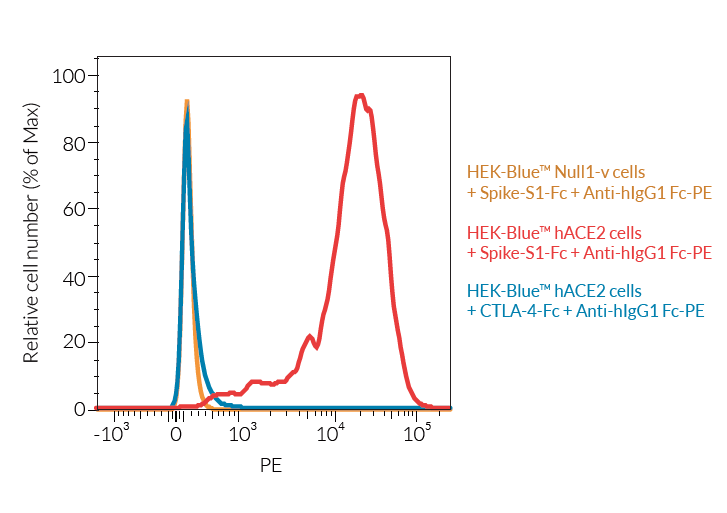
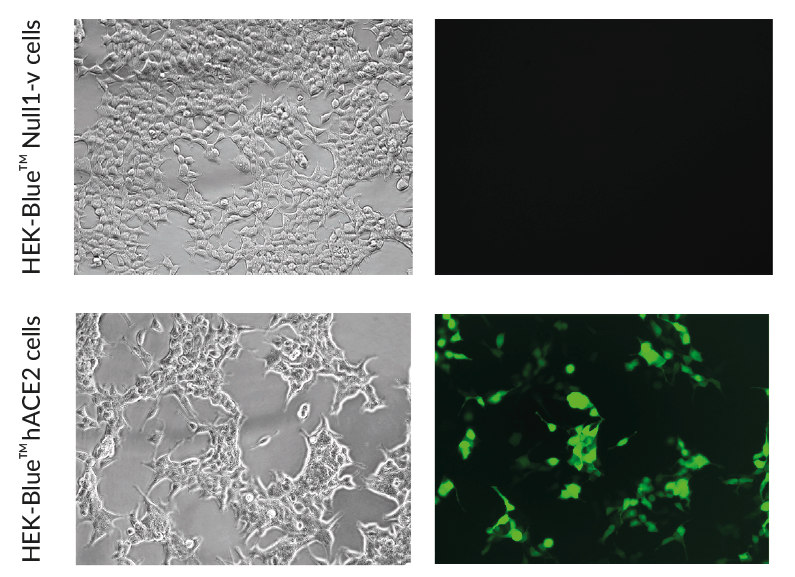
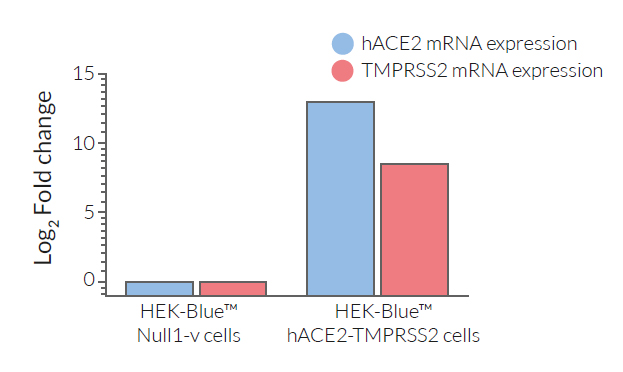
These cells have been engineered to stably overexpress the host SARS-CoV-2 receptors, human (h)ACE2, and TMPRSS2 [1]. They were generated from HEK‑Blue™ Null1‑v cells, which express an NF-κB inducible SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) reporter gene.
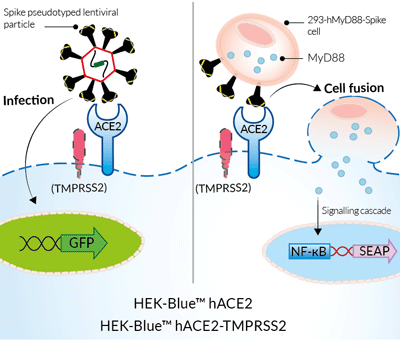
Studying infection and cell fusion with
HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 cells
 Available upon request:
Available upon request:
• HEK-Lucia™ hACE2 Cells
• HEK-Lucia™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 Cells
• HEK-hACE2 Cells
• HEK-hACE2-TMPRSS2 Cells
Sensitive to SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19), gains entry into host cells through the interaction of the viral Spike protein with the host ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors [1]. HEK293-derived cells are poorly permissive to infection by SARS-CoV-2 or Spike pseudotyped lentiviral particles. Therefore, to increase their permissivity HEK-Blue™ Null1-v cells have been stably transfected with ACE2 only, or ACE2 and TMPRSS2. In contrast to HEK-Blue™ Null1-v cells, HEK-Blue™ hACE2(‑TMPRSS2) cells are sensitive to Spike pseudotyped lentiviral particles. Notably, the addition of TMPRSS2 increases the cell line’s infectivity.
For studying Spike-ACE2-dependent cell fusion
These HEK-293-derived SARS-COV-2 permissive reporter cells can be used as ‘acceptor’ cells in InvivoGen’s SARS-CoV-2 Spike-ACE2 dependent cell fusion assay. This relies on the transfer of the TLR/IL-1 adaptor molecule, MyD88, from a 'donor cell line' (293-hMyD88 transfected with a Spike expression plasmid) to an 'acceptor cell line' expressing an NF-κB-SEAP-inducible reporter gene. Cell fusion is readily assessable in the co-culture supernatant using the SEAP detection reagent, QUANTI‑Blue™ Solution. Unlike infection by pseudotyped particles, the presence of TMPRSS2 does not have an effect on cell fusion in this assay.
Key features
- Verified overexpression of human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 genes
- Permissive and sensitive to SARS-COV-2 Spike pseudotyped lentiviral particles
- Functionally tested in InvivoGen’s cell fusion assay with SARS-CoV-2 Spike-expressing hMyD88 cells.
- Readily assessable NF-κB-dependent SEAP reporter activity
Applications
- Screening inhibitors of Spike-binding and/or its host receptors (i.e. ACE2 and TMPRSS2).
- Studying the efficacy of the vaccines and/or current therapeutics (e.g. mAbs) against the emerging variants by infection studies with pseudotyped particles or cell fusion assays.
InvivoGen has also generated:
➔ HEK-Lucia™ hACE2 and HEK-Lucia™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 cells featuring an NF-KB-inducible Lucia luciferase reporter for a larger detection range than the colorimetric SEAP assays.
➔ HEK-hACE2 and HEK-hACE2-TMPRSS2 cells with no reporter activity for infection, pseudoparticle transduction, or qualitative fusion assays.
These cells have been used to compare the efficiency of SARS-CoV2 Spike variant-mediated cellular infection and fusion. See data
![]() Learn more about SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential therapeutics
Learn more about SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential therapeutics
References
1. Hoffmann M. et al., 2020. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 181:1-16.
2. Zhou P. et al., 2020. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 579(7798):270-273.
3. Walls A.C. et al., 2020. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell. 181(2):281-292.e6.
Specifications
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/L glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Antibiotic resistance:
- HEK-Blue™ hACE2: Puromycin and Zeocin®
- HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2: Hygromycin B Gold, Puromycin and Zeocin®
Quality Control
- ACE2 gene expression has been verified by RT-qPCR, FACS staining, and functional assays.
- TMPRSS2 gene expression has been verified by RT-qPCR and functional assays.
- Activation of the NF-κB response has been verified upon stimulation with various inducers (e.g. TNF-α).
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified for HEK-Blue™ hACE2 and HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
InvivoGen's products are covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions).
Back to the topContents
Please note: Each cell line is sold separately. See TDS for the exact contents of each cell line.
HEK-Blue™ hACE2 cells
- 3-7 x 106 HEK-Blue™ hACE2 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Puromycin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 cells
- 3-7 x 106 HEK-Blue™ hACE2-TMPRSS2 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Puromycin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Hygromycin B Gold (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
ACE2 BACKGROUND
ACE2 plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) by facilitating viral entry through its interaction with the Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) [1]. Following this, host proteases (e.g. transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2)) cleave the S protein into two functional subunits (S1 and S2), allowing virus-host membrane fusion, and the release of viral contents (e.g. RNA) into the cytosol [1-3]. Notably, TMPRSS2 is not needed for infection of HEK293 cells by SARS-CoV-2 spike-pseudotyped lentiviral particles [4, in-house data].
References
1. Zhou P. et al., 2020. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 579(7798):270-273.
2. Hoffmann M. et al., 2020. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 181:1-16.
3. Walls A.C. et al., 2020. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell. 181(2):281-292.e6.
4. Korber B. et al., 2020. Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2-Spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043.