HepG2-Lucia™ AhR Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HepG2-Lucia™ AhR Cells Human HepG2 liver carcinoma - AhR-Lucia reporter cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hpgl-ahr
|
|
||
|
HepG2-Lucia™ AhR vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hpgl-ahr-av
|
Notification: Reference #hpgl-ahr-av can only be ordered together with reference #hpgl-ahr.
Human HepG2 liver carcinoma - AhR-Lucia reporter cells
HepG2-Lucia™ AhR cells are engineered from the human HepG2 hepatoma cell line for the study of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) genomic signaling induction (see details), by monitoring the activity of the Lucia luciferase reporter protein.
AhR is a ligand-dependent transcriptional factor widely expressed in barrier tissues. Notably, AhR plays an important role in gut microbiota and the host's immune homeostasis [1].
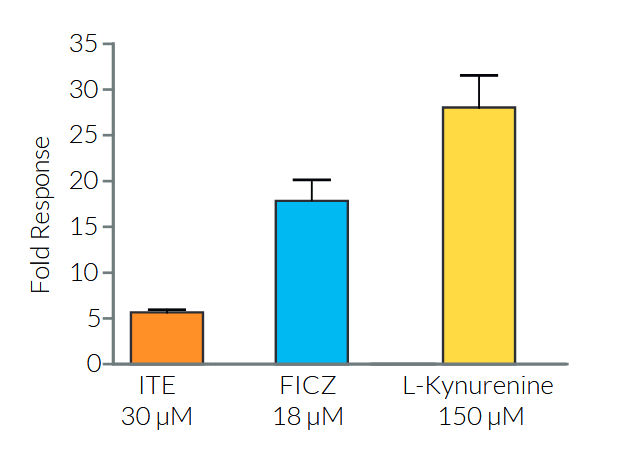
HepG2-Lucia™ AhR cells, which express endogenous AhR, are highly relevant for the detection/screening of AhR ligands in food or environmental samples [2].
These cells express the secreted Lucia luciferase reporter gene under the control of a minimal promoter coupled with the human Cyp1a1 gene's entire regulatory sequence, which contains six dioxin-responsive elements (DREs).
As a result, these cells allow studying the AhR genomic signaling pathway, by monitoring the activity of Lucia luciferase in the cell culture supernatant when using the QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia detection reagent.
HepG2-Lucia™ AhR cells are resistant to Zeocin®.
![]() Read our review on AhR's key role in intestinal microbiota and immunity.
Read our review on AhR's key role in intestinal microbiota and immunity.
References
1. Lamas B. et al. 2018. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and intestinal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 11:1024-38.
2. Gao J. et al. 2018. Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 8:13.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistances: Zeocin®
Quality Control:
- Reporter activity has been verified by functional assays.
- The stability of this cell line for 20 passages following thawing has been verified.
- HepG2-Lucia™ AhR cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 of HepG2-Lucia™ AhR cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Details
The aryl hydrocarborn receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcriptional factor widely expressed in barrier tissues [1]. AhR plays a key role in gut-microbiota and host’s immune homeostasis, not only in the intestine but also at distant sites [1].
Besides xenobiotics, including the prototypic AhR agonist 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a variety of dietary-derived AhR ligands have been identified, many of which are byproducts of tryptophan (Trp) metabolism [2].
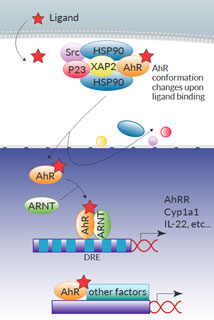
Inactive AhR resides in the cytoplasm within a Hsp90:XAP2:p23:Src protein complex. The AhR canonical genomic signaling pathway occurs as follows: upon ligand binding, the complex undergoes conformational changes and translocates into the nucleus. AhR heterodimerizes with AhR nuclear translocator (ARNT) before binding to dioxin response elements (DREs) in the upstream regulatory regions of AhR target genes, such as the cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase Cyp1a1, the AhR repressor (AhRR), and the IL-22 interleukin.
Of note, non-canonical AhR signaling pathways have also been reported, either at the genomic level through association with other transcription factors (e.g. NF-κB), or at the non-genomic level (e.g. through the release of the Src kinase) [2,3].
References
1. Lamas B. et al. 2018. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and intestinal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 11:1024-38.
2. Gao J. et al. 2018. Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 8:13.
3. Park JH. et al., 2018. Kynurenine promotes the goblet cell differentiation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells by modulating Wnt, Notch and AhR signals. Oncol Rep. 39(4):1930-8.