A549-Dual™ Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A549-Dual™ Cells Human NF-κB-SEAP & IRF-Luc Reporter lung carcinoma |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
a549d-nfis
|
|
||
|
A549-Dual™ vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
a549d-nfis-av
|
Notification:
Reference #a549d-nfis-av can only be ordered together with reference #a549d-nfis.
Human NF-κB-SEAP & IRF-Luc Reporter lung carcinoma
A549-Dual™ cells are adherent epithelial cells that have been derived from the human A549 lung carcinoma cell line by stable integration of two inducible reporter constructs. The A549 cell line is a well-characterized cellular model for asthma, allergies and respiratory infections.
A549-Dual™ cells express a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene under the control of the IFN-β minimal promoter fused to five NF-κB binding sites.
A549-Dual™ cells also express the Lucia luciferase gene, which encodes a secreted luciferase, under the control of an ISG54 minimal promoter in conjunction with five IFN-stimulated response elements.
As a result, A549-Dual™ cells allow to simultaneously study the NF-κB pathway, by assessing the activity of SEAP, and the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) pathway, by monitoring the activity of Lucia luciferase.
Both reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent, and QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia and Gaussia luciferase detection reagent.
Back to the topSpecifications
Antibiotic resistances: Zeocin® and blasticidin
Guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Quality Control:
- The stability of this cell line for 20 passages following thawing has been verified.
- For each lot, proper activation of the NF-κB pathway and IRF pathway is confirmed upon stimulation of A549-Dual™ cells by various pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) known to activate these pathways.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 of A549-Dual™ cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Description
A549-Dual™ cells express numerous pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) RIG-I [1, 2], and the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) TLR2 [3], TLR3 [4, 5] and TLR5 [6] but not TLR4 [3].
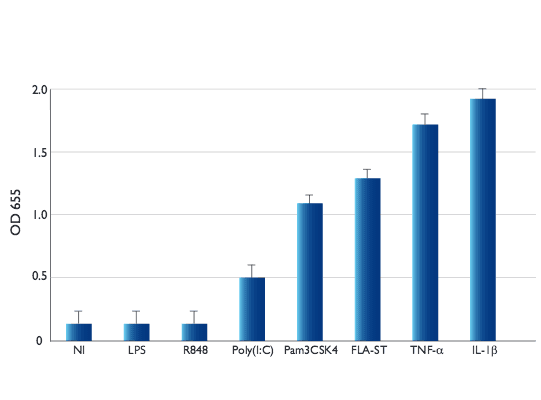
Upon recognition of their cognate PAMPs, these receptors induce signaling pathways leading to the activation of the transcription factors NF-kB and/or IRF3/7. Stimulation of A549-Dual™ cells with the following PAMPs, Pam3CSK4 (TLR2) Poly(I:C) (TLR3), flagellin (TLR5), leads to the activation of NF-kB. IL-1b or TNF-a can be used as positive controls to activate the NF-kB signaling pathway.
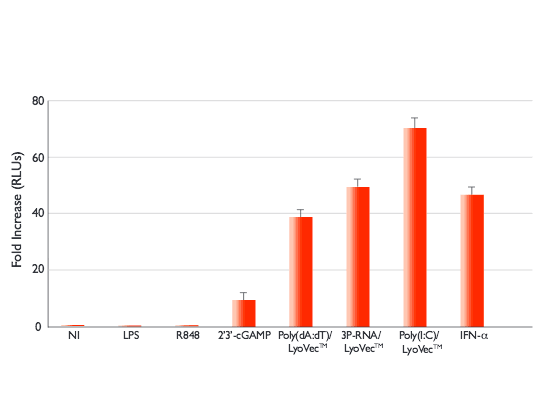
Stimulation with RLR ligands, such as transfected poly(I:C) or poly(dA:dT), or the STING agonist, 2’3’-cGAMP, triggers the IRF pathway. IFN-a can be used as positive controls to activate the IRF signaling pathway.
A549-Dual™ cells are resistant to the selectable markers blasticidin and Zeocin™.
1. Kolokoltsova OA. et al., 2014. RIG-I enhanced interferon independent apoptosis upon Junin virus infection. PLoS One. 9(6):e99610.
2. Hagmann CA. et al., 2013. RIG-I detects triphosphorylated RNA of Listeria monocytogenes during infection in non-immune cells. PLoS One. 8(4):e62872.
3 Slevogt H. et al., 2007. Moraxella catarrhalis is internalized in respiratory epithelial cells by a trigger-like mechanism and initiates a TLR2- and partly NOD1-dependent inflammatory immune response. Cell Microbiol. 9(3):694-707.
4. Taura M. et al., 2008. p53 regulates Toll-like receptor 3 expression and function in human epithelial cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 28(21):6557-67.
5. Tissari J. et al., 2015. IFN-alpha enhances TLR3-mediated antiviral cytokine expression in human endothelial and epithelial cells by up-regulating TLR3 expression J Immunol. 174(7):4289-94.
6. Tallant T. et al., 2004. Flagellin acting via TLR5 is the major activator of key signaling pathways leading to NF-kappa B and proinflammatory gene program activation in intestinal epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 4:33.