A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 Cells MDA-5 knockout NF-kB-SEAP & IRF-Lucia Reporter Cell Line |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
a549d-komda5
|
|
||
|
A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
a549d-komda5-av
|
Notification:
Reference #a549d-komda5-av can only be ordered together with reference #a549d-komda5.
MDA-5 knockout NF-kB-SEAP & IRF-Lucia Reporter Cell Line
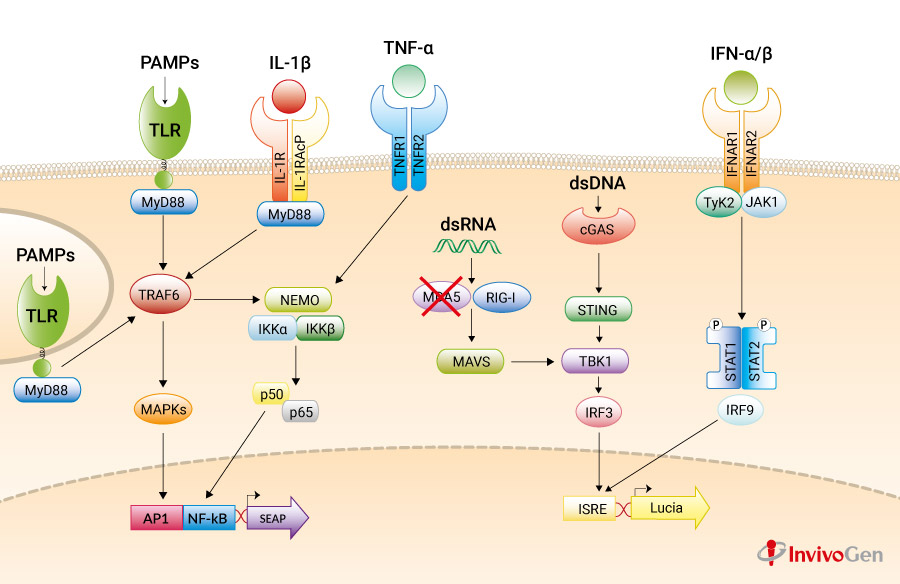
A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 cells were generated from A549-Dual™ cells through the stable knockout of the MDA5 gene. They are adherent epithelial cells derived from the human A549 lung carcinoma cell line by stable integration of two inducible reporter constructs. The A549 cell line, a cellular model for asthma and respiratory infections, expresses many pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including RIG-I [1, 2], and the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) TLR2 [3], TLR3 and TLR5 but not TLR4 [3].
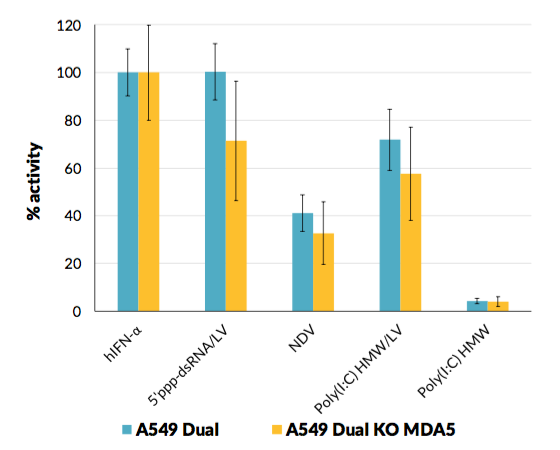
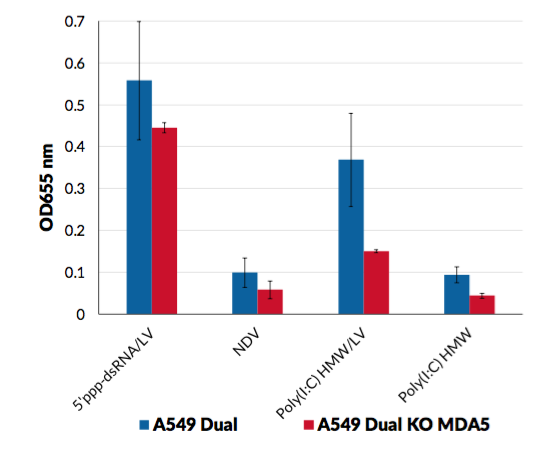
A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 and A549-Dual™ cells express a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene under the control of the IFN-β minimal promoter fused to five NF-κB binding sites. They also express the secreted Lucia luciferase reporter gene under the control of an ISG54 minimal promoter in conjunction with five IFN-stimulated response elements. As a result, they allow to simultaneously study the NF-kB pathway, by assessing the activity of SEAP, and the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) pathway, by monitoring the activity of Lucia luciferase. Both reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI- Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent, and QUANTI‑Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia and Gaussia luciferease detection reagent.
A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 cells are resistant to blasticidin and Zeocin®.
References:
1. Kolokoltsova OA. et al., 2014. RIG-I enhanced interferon independent apoptosis upon Junin virus infection. PLoS One. 9:e99610.
2. Hagmann CA. et al., 2013. RIG-I detects triphosphorylated RNA of Listeria monocytogenes during infection in non-immune cells. PLoS One. 8:e62872.
3. Slevogt H. et al., 2007. Moraxella catarrhalis is internalized in respiratory epithelial cells by a trigger-like mechanism and initiates a TLR2- and partly NOD1-dependent inflammatory immune response. Cell Microbiol. 9(3):694-707.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®, blasticidin
Growth Medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Freezing Medium: DMEM with 20% FBS and 10% (v/v) DMSO
Test Medium for use with QUANTI-Blue™: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated FBS (30 min at 56°C), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin
Quality control:
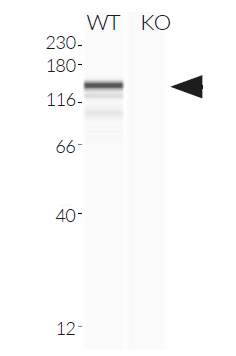
- MDA-5 knockout has been verified by functional assays and DNA sequencing.
- The stability of this cell line for 20 passages following thawing has been verified.
- A549-Dual™ KO-MDA5 cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Description
MDA-5 (melanoma-differentiation-associated gene 5, also known as Ifih1 or Helicard) is a cytoplasmic RNA helicase that plays an important role in antiviral response. It senses double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), a replication intermediate for RNA viruses, leading to production of type I interferons (IFNs) in infected cells. MDA-5 and the related RNA helicase RIG-I recognize a complementary set of cytosolic viral dsRNA. However, some viruses such as picornaviruses appear to activate only MDA-5. Interestingly, transfected poly(I:C), a synthetic analog of viral dsRNA, is recognized by both MDA-5 and RIG-I.