TLR2 signaling inhibitor
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TL2-C29 Human TLR2/1 & TLR2/6, murine TLR2/1 signaling inhibitor |
Show product |
5 mg |
inh-c29
|
|
Inhibitor of TLR2 signaling
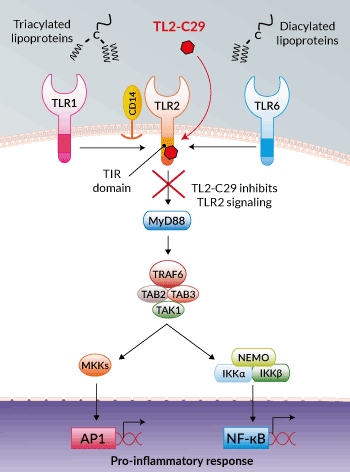
Inhibition of TLR2 signaling by TL2-C29
TL2-C29 is a small-molecule inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) [1]. TLR2 plays an essential role in detecting a diverse range of microbial pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) from bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses [2]. TLR1 and TLR6 co-receptors are crucial for TLR2 signaling and ligand specificity. Cell surface TLR2/TLR1 and TLR2/TLR6 heterodimers bind tri- and diacylated lipoproteins, respectively [3,4]. TLR2 signaling is initiated by ligand-induced dimerization of the essential cytoplasmic TIR (Toll/interleukin-1 receptor) domains of the TLR2 heterodimers and adapter proteins. Subsequent signaling cascades lead to a pro-inflammatory response.
Mode of action:
TL2-C29 binds a pocket in the BB loop within the TLR2 TIR domain, thereby inhibiting TLR2 interaction with the MyD88 adapter molecule and downstream MAPK and NF-κB activation [1]. In human TLR2 signaling, TL2-C29 blocks both TLR2/1 and TLR2/6 pathways. In murine TLR2 signaling, TL2-C29 preferentially inhibits the TLR2/1 pathway [1, and in-house data].
Key features:
- Potent inhibitor of human TLR2/1 and TLR2/6 signaling
- Potent inhibitor of murine TLR2/1 signaling
- No substantial cellular toxicity
- Inhibition of NF-κB/AP-1 signaling validated in cellular assays
- InvitroFit™ grade: each lot is highly pure (≥ 95%) and functionally tested
![]() Learn more about TLR2 heterodimers.
Learn more about TLR2 heterodimers.
References:
1. Mistry, P. et al., 2015. Inhibition of TLR2 signaling by small molecule inhibitors targeting a pocket within the TLR2 TIR domain. PNAS. 112(17):5455-5460.
2. Oliveira-Nascimento L. et al., 2012. The role of TLR2 in infection and Immunity. Front Immunol. 3(79): doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00079.
3. Takeuchi O. et al., 2001. Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol. 13: 933-940.
4. Takeuchi O. et al., 2002. Cutting edge: role of Toll-like receptor 1 in mediating immune response to microbial lipoproteins. J Immunol. 169: 10-14.
Specifications
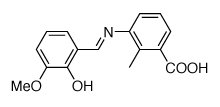
Synonyms: C29; TLR2-IN-C29; 3-[[(2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methylene]amino]-2-methyl-benzoic acid
CAS number: 363600-92-4
Formula: C16H15NO4
Molecular weight: 285.3 g/mol
Solubility: 50 mM (14.3 mg/ml) in DMSO
Working concentration: 25 - 200 µM for cell culture assays.
Quality control:
- Purity ≥ 95% (NMR)
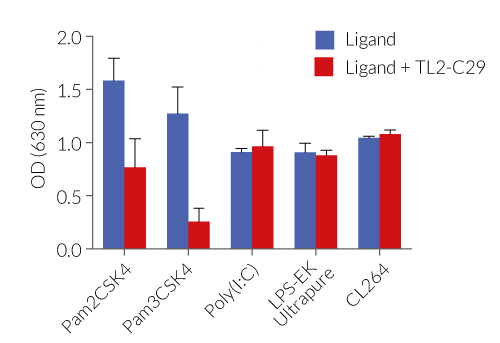
- Inhibition of human TLR2/1 and TLR2/6 signaling has been confirmed using cellular assays
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Contents
- 5 mg TL2-C29 (provided as a dried powder)
![]() TL2-C29 is shipped at room temperature.
TL2-C29 is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Store at -20°C.
Store at -20°C.
![]() The resuspended product is stable for 2 months when properly stored.
The resuspended product is stable for 2 months when properly stored.
![]() Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Details
TL2-C29 chemical structure (CAS 363600-92-4)
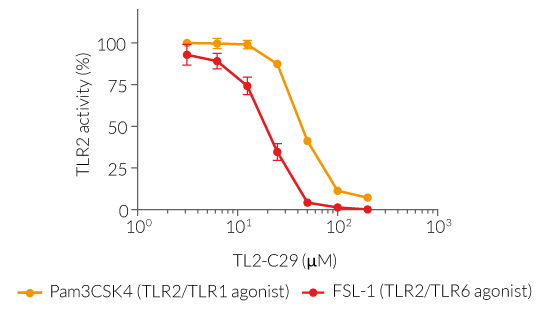
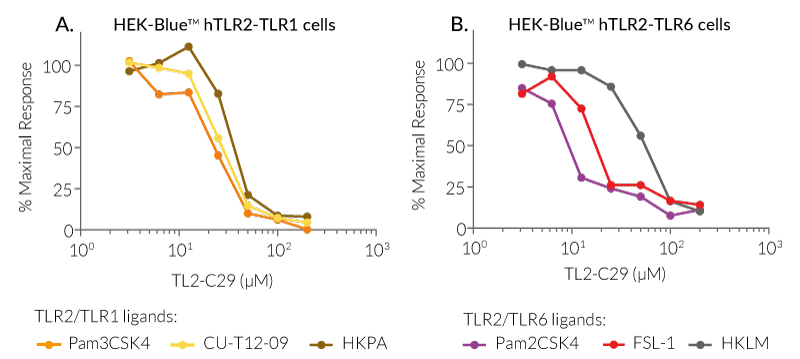
TL2-C29 is a potent inhibitor of human TLR2/1 and TLR2/6 signaling, and preferentially inhibits murine TLR2/1 signaling
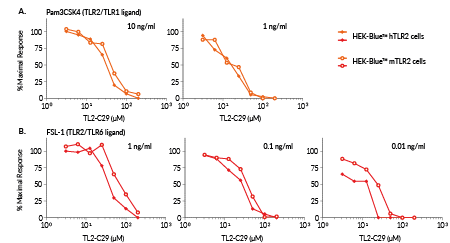
Inhibition of TLR2 signaling by TL2-C29
TL2-C29 has been described to mediate a TLR2 signaling inhibition in a species-dependent manner between humans and mice [1].
We assessed the species-specific inhibition potency of TL2-C29 using HEK-Blue™ hTLR2 and HEK-Blue™ mTLR2 cells, stably expressing human TLR2 and mouse TLR2, respectively (see Figure). We observed that TL2-C29-mediated inhibition of TLR2/TLR1 signaling is highly similar in cells expressing hTLR2 or mTLR2, using two doses of Pam3CSK4 (panel A). However, TL2-C29-mediated inhibition of TLR2/TLR6 signaling is stronger in cells expressing hTLR2 than in cells expressing mTLR2, especially at a low dose of FSL-1 (panel B).
1. Mistry, P. et al., 2015. Inhibition of TLR2 signaling by small molecule inhibitors targeting a pocket within the TLR2 TIR domain. PNAS. 112(17):5455-5460.
Back to the top