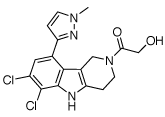
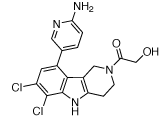
Human cGAS inhibitor
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
G140 Human cGAS inhibitor - InvitroFit™ |
Show product |
2 mg 5 x 2 mg |
inh-g140
|
|
Specific inhibitor of human cGAS
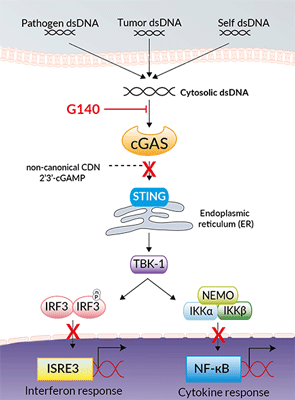
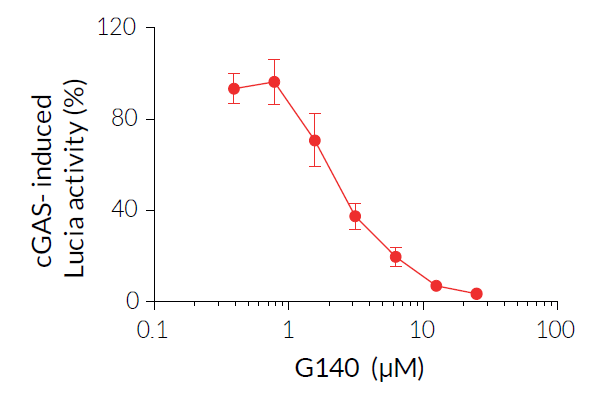
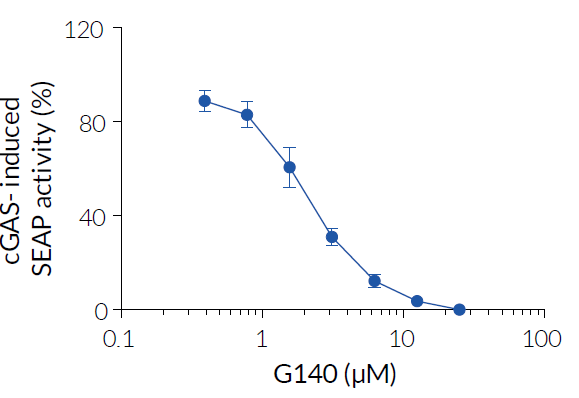
Inhibition of human cGAS signaling by G140
G140 is a small-molecule inhibitor of human cGAS (cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; cGAMP synthase). cGAS is the primary sensor of cytosolic double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) originating either from pathogenic infections, mitochondrial dsDNA misprocessing, or micronuclei rupture. Direct DNA binding to cGAS catalyzes the production of 2', 3'-cGAMP, a cyclic dinucleotide, which in turn activates the STING pathway, resulting in IRF (interferon regulatory factor) and NF‑κB-mediated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and type-I interferons [2-4].
G140 is a promising probe for the development of drugs targeting human cGAS for preventing auto-inflammation and treating interferonopathies [5]. G140 was co-developed along with another chemotype, G150, and both molecules display similar potency at inhibiting cGAS [1].
![]() More details
More details
Mode of action:
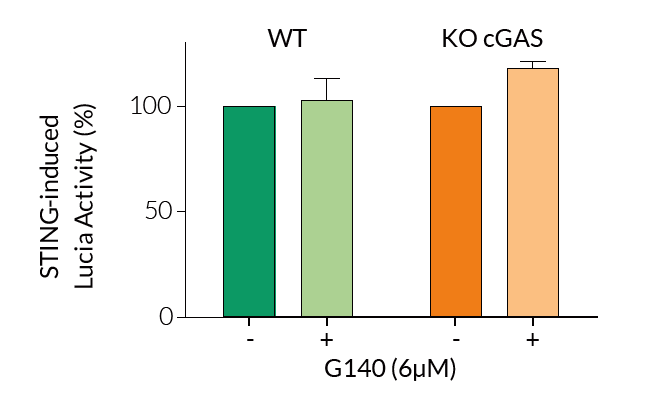
Co-crystallization studies with another lead compound, G150, revealed that the small molecule targets the human cGAS catalytic pocket, competing with cGAS substrates ATP/GTP, thereby inhibiting the synthesis of 2', 3'-cGAMP [1, 4].
Key features:
- Potent and selective inhibitor of human cGAS
- No substantial cellular toxicity [1]
- Inhibition of IRF and NF-κB signaling validated in cellular assays
- InvitroFit™ grade: each lot is highly pure (≥95%) and functionally tested
Note: InvivoGen also offers RU.521, a specific inhibitor of murine cGAS.
References:
1. Lama, L. et al., 2019. Development of human cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors for repression of dsDNA-triggered interferon expression. Nat Commun 10, 2261.
2. Gao, D. et al., 2015. Activation of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase by self-DNA causes autoimmune diseases. PNAS 112, E5699-5705.
3. Abe, T. et al., 2014. Cytosolic-DNA-mediated, STINGdependent proinflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-kappaB activation through TBK1. J Virol 88, 5328-5341.
4. Hertzog, J. & Rehwinkel J., 2020. Regulation and inhibition of the DNA sensor cGAS. EMBO Reports 21(12):e51345.
5. Tan J. et al., 2021. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of Tetrahydro-γ-carboline derivatives as potent anti-inflammatory agents targeting cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. J. Med Chem. 64(11):7667-7690.
Specifications
Formula: C17H16Cl2N4O2
Molecular weight: 379.24 g/mol
Solubility: 5 mg/ml (13.18 mM) in DMSO
Working concentration: 1 - 20 µM for cell culture assays.
Quality control:
- Purity ≥ 95% (UHPLC).
- Inhibition of cGAS has been confirmed using cellular assays
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Contents
G140 is available in two quantities:
- inh-g140: 2 mg
- inh-g140-5: 5 x 2 mg
![]() G140 is shipped at room temperature.
G140 is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, store at -20°C.
Upon receipt, store at -20°C.
Back to the top
Details
G140 and G150 are two small molecules that have been chemically optimized from the same parent compound to potently and specifically inhibit human cGAS [1]. G140 and G150 feature a methyl-pyrazole and a 2-aminopyridine moiety, respectively.
- They both show no substantial cellular toxicity and similar cellular IC50 when measuring the expression of ISGs (interferon-stimulated genes) in human THP-1 monocytes or primary human macrophages [1].
- A 50 to 100 fold concentration difference between LD50 and IC50 provides a significant window between efficacy and toxicity for drug testing [1].
- G150 with human cGAS co-crystallization reveals that the inhibitor (and at least one related chemotype) binds to the enzyme catalytic pocket [1].
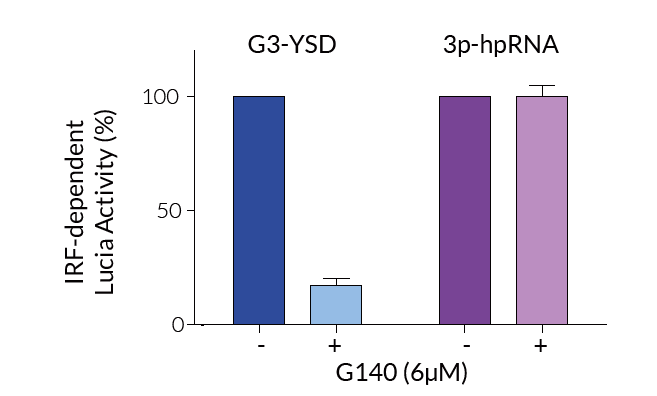
- G140 efficiently inhibits IRF signaling induced by dsDNA of different lengths in a dose-dependent manner [1].
- G140 has been used as a reference compound in developing highly potent small-molecule inhibitors of cGAS to treat inflammatory diseases [2].
1. Lama, L. et al. 2019. Development of human cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors for repression of dsDNA-triggered interferon expression. Nat Commun 10, 2261.
2. Tan J. et al., 2021. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of Tetrahydro-γ-carboline derivatives as potent anti-inflammatory agents targeting cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. J. Med Chem. 64(11):7667-7690.