BMS-986256 (Afimetoran)
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
BMS-986256 TLR7/TLR8 inhibitor - InvitroFit™ |
Show product |
2 mg |
inh-afi
|
|
Specific TLR7 and TLR8 dual inhibitor
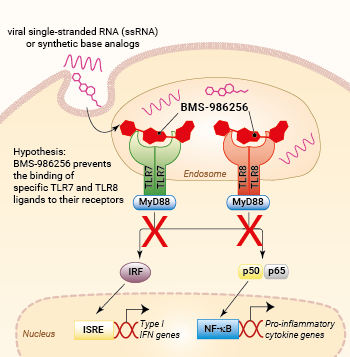
Inhibition of TLR7 and TLR8 signaling by BMS-986256
BMS-986256 (Afimetoran) is an indole-based small molecule that functions as a dual and selective inhibitor of TLR7 and TLR8 [1, 2]. Its potency has been demonstrated in various in vitro assays and a mouse lupus model in vivo [1, 2]. BMS-986256 is currently under phase II clinical investigation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [3, 4].
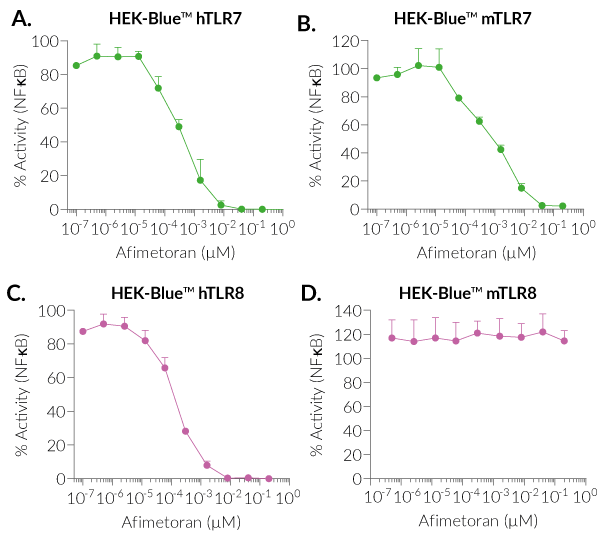
BMS-986256 efficiently inhibits human (h)TLR7, mouse (m)TLR7, and hTLR8, but not mTLR8, as assessed using InvivoGen's HEK-Blue™ reporter cell lines overexpressing hTLR7, mTLR7, hTLR8, and mTLR8 (see figures).
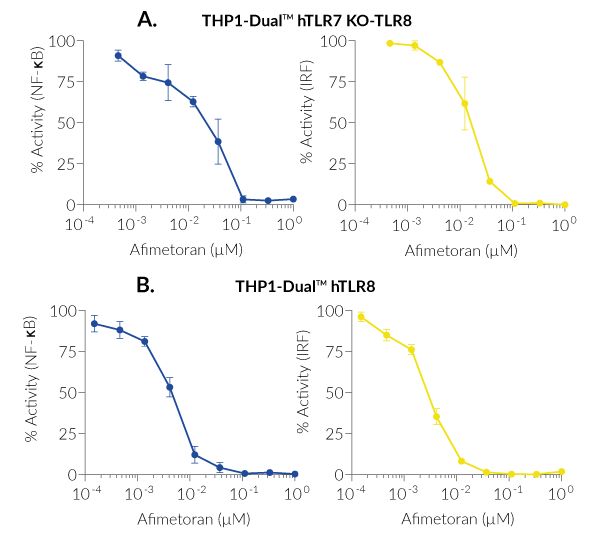
BMS-986256 exerts inhibitory actions on both NF-κB and IRF pathways downstream hTLR7 and hTLR8, as assessed with THP1-Dual™-derived cells (see figures).
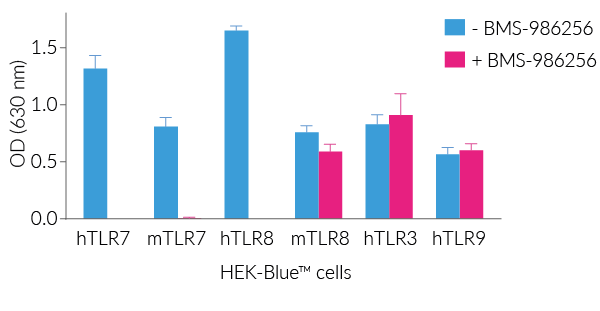
Importantly, BMS-986256 blocks the activation of TLR7 and TLR8 with no effect on other endosomal TLRs, i.e. TLR3 and TLR9 (see figures).
Mode of action
The specific binding mechanism of BMS-986256 is not known yet. However, it is hypothesized to behave similarly to other TLR7/8 antagonists by maintaining the inactive conformation of TLR7 and TLR8 receptors [2, 5]. Future research is needed to elucidate the exact mode of action of BMS-986256.
Key features of BMS-986256
- Indole-based small molecule
- Dual and selective inhibitor of TLR7- and TLR8-mediated NF-κB and IRF pathways
- Potent inhibitor of human TLR7, human TLR8, and mouse TLR7
- No action on mouse TLR8 overexpressed in HEK-Blue™ cells
- InvitroFit™: each lot of BMS-986256 is highly pure (≥95%) and functionally tested.
References:
1. Bristol-Myers Squibb company. 04.01.2018. WO 2018/005586 A1. [1,2,4] Triazolo [1,5-A] Pyridinyl substituted indole compounds.
2. Zheng H. et al., 2023. Recent Advances on Small-Molecule Antagonists Targeting TLR7. Molecules 28 (2), pp.634. ff10.3390/molecules28020634ff. ffhal-04564284.
3. Kalliokas. et al., 2021. Targeting TLR Signaling Cascades in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Update. Biomedicines 12(1):138.
4. NCT04895696. www.clinicaltrials.gov. As accessed in October 2024.
5. Vlach J. et al., 2020. Discovery of M5049: a novel selective Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 inhibitor for treatment of autoimmunity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 376:397.
Specifications
CAS number: 2171019-55-7
Formula: C26H32N6O
Molecular weight: 444.57 g/mol
Solubility: 11.25 mM (5 mg/ml) in DMSO
Working concentration:
- in vitro: 2 nM - 1 μM for cellular assays, depending on cell type and agonist (see figures).
- in vivo: 0.25 mg/kg - 2.5 mg/kg, oral gavage, once daily, in NZB/W mouse model of lupus [1].
Quality control:
- Purity: ≥95% (UHPLC)
- The inhibition of human TLR7 by BMS-986256 is confirmed using HEK-Blue™ hTLR7 cells.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ hTLR2 and HEK-Blue™ hTLR4 cells.
Reference:
1. Bristol-Myers Squibb company. 04.01.2018. WO 2018/005586 A1. [1,2,4] Triazolo [1,5-A] Pyridinyl substituted indole compounds.
Back to the topContents
- 2 mg of lyophilized BMS-986256
![]() BMS-986256 is shipped at room temperature.
BMS-986256 is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, store BMS-986256 at -20 °C. Upon resuspension of BMS-986256 in DMSO, prepare aliquots and store them at -20 °C.
Upon receipt, store BMS-986256 at -20 °C. Upon resuspension of BMS-986256 in DMSO, prepare aliquots and store them at -20 °C.
![]() The resuspended product is stable for 1 month when properly stored.
The resuspended product is stable for 1 month when properly stored.
![]() Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Details
TLR7 and TLR8 are both activated by single-stranded (ss)RNA and RNA molecules found in immune complexes with RNA protein-binding autoantibodies [1]. Thus, these two TLRs play a beneficial role in clearing microbial infections, but they can also contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases such as cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus (CLE/SLE) [1-3]. In addition, it is postulated that TLR7/8 may play a role in the cytokine storm in severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia [2, 3].
BMS986256 is described as an equipotent dual TLR7/TLR8 inhibitor using in vitro cellular assays [4]. However, in-house data suggest that the in vitro potency for each inhibitor depends on the choice of TLR7/TLR8-expressing cell lines and the type of agonists.
BMS986256 is currently under investigation as an oral treatment for SLE [5]. Interestingly, BMS-986256 demonstrates steroid-sparing effects in a mouse lupus model, a key feature that could help overcome glucocorticoid resistance and side effects in SLE patients [6].
Chemical structure of BMS-986256
References:
1. Vlach J. et al., 2020. Discovery of M5049: a novel selective Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 inhibitor for treatment of autoimmunity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 376:397.
2. Port A. et al., 2021. Phase 1 study in healthy participants of the safety, pharmacokinectics, and pharmacodynamics of enpatoran (M5049), a dual antagonist of toll-like receptors 7 and 8. Pharmacol Res Perspect 9(5):e00842.
3. Klopp-Schulze I. et al. 2022. Applying Modeling and Simulations for Rational Dose Selection of Novel Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 Inhibitor Enpatoran for Indications of High Medical Need. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 112: 297-306.
4. Bristol-Myers Squibb company. 04.01.2018. WO 2018/005586 A1. [1,2,4] Triazolo [1,5-A] Pyridinyl substituted indole compounds
5. NCT04895696. www.clinicaltrials.gov. As accessed in October 2024.
6. Dudhgaonkar S, et al., 2023. AB0132 Afimetoran (BMS-986256), an equipotent TLR7/8 antagonist, demonstrates steroid-sparing effects in a lupus mouse model. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 82:1245-1246.