STING inhibitor
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
H-151 Synthetic Indole Derivative - STING Inhibitor - InvitroFit™ |
Show product |
10 mg 5 x 10 mg |
inh-h151
|
|
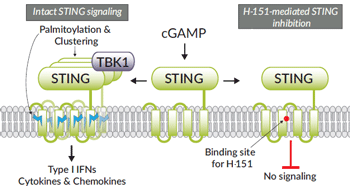
Mechanism of action of H-151-mediated STING inhibition
STING inhibitor
H-151 is a potent, irreversible, and selective small-molecule inhibitor of STING [1], a key sensor of cytosolic nucleic acids. STING is a transmembrane protein found in the endoplasmic reticulum. Upon activation, it functions as a signaling hub, orchestrating immune responses to pathogenic, tumoral, or self-DNA detected in the cytoplasm [2].
Mode of action:
H-151 exerts its inhibitory action by covalently binding to STING at the transmembrane cysteine residue at position 91. This synthetic indole-derivative blocks STING palmitoylation and clustering, two essential steps for STING signaling. In models of autoinflammatory disease, H-151 blocks STING‑induced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduces inflammation [1].
Key features:
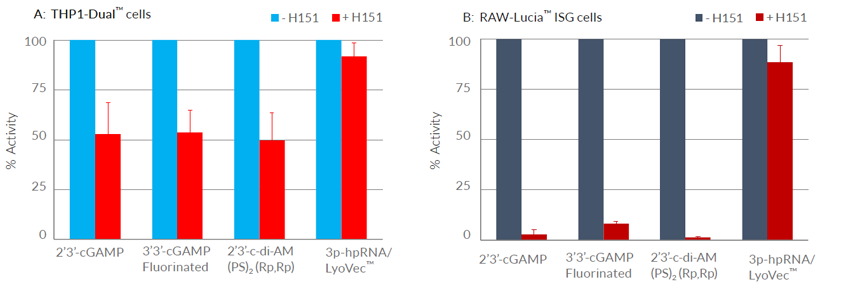
- H-151 potently inhibits both human and murine STING, in vitro and in vivo (mouse models)
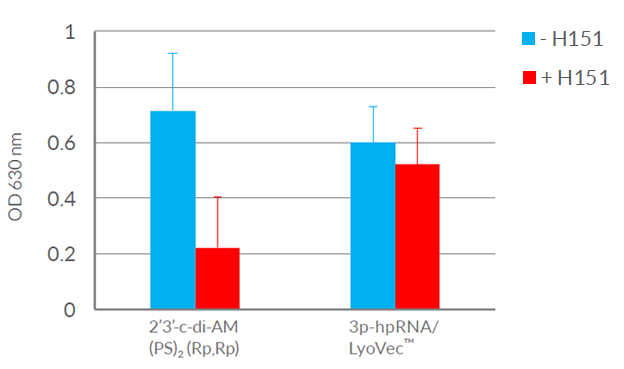
- H-151 strongly reduces STING-mediated but not RIG-I-mediated Interferon-β production
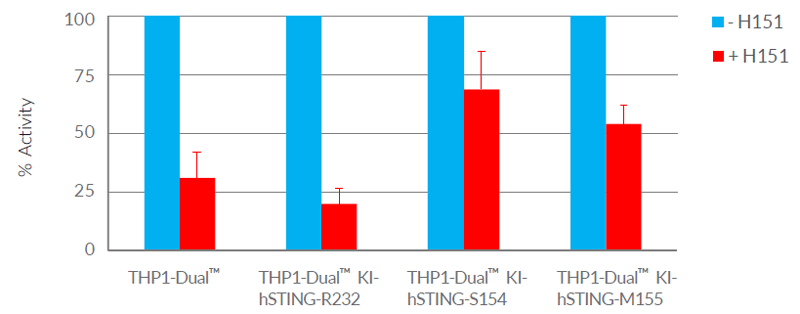
- H-151 blocks the activity of all STING variants tested
- InvitroFit™ grade: each lot is highly pure (≥95%) and functionally tested
![]() Read our review: Follow the path to STING
Read our review: Follow the path to STING
References:
1. Haag S.M. et al., 2018. Targeting STING with covalent small-molecule inhibitors. Nature 559:269-73.
2. Ishikawa H. & Barber G.N. 2008. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455:674-8.
Specifications
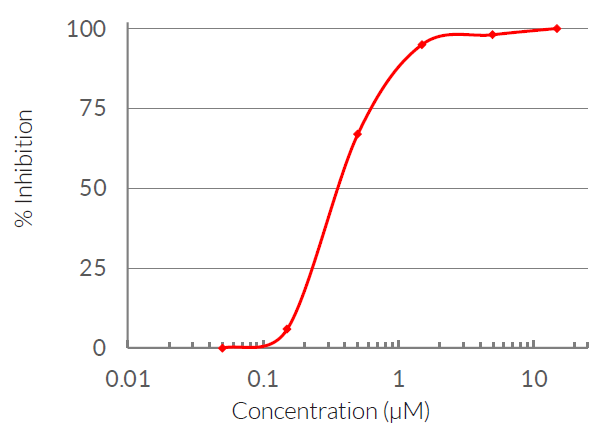
Working concentration: 4 ng/ml (15 nM) to 4 μg/ml (15 μM) for cell culture assays
CAS number: 941987-60-6
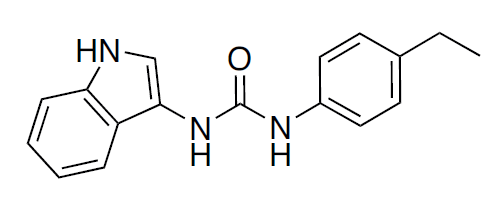
Synonym: N-(4-Ethylphenyl)-N’-1H-indol-3-yl-urea
Solubility: 20 mg/ml (71.60 mM) in DMSO
Formula: C17H17N3O
Molecular weight: 279.34 g/mol
Quality control:
- Purity ≥ 95% (UHPLC)
- The inhibitory activity has been validated using cellular assays.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK-Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Contents
H-151 is available in two quantities:
- inh-h151: 10 mg
- inh-h151-5: 5 x 10 mg
![]() H-151 is shipped at room temperature.
H-151 is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, store at -20°C.
Upon receipt, store at -20°C.
Back to the top