Human TLR2 HEK293 Reporter Cells (NF-κB and IL-8)
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 Cells Human TLR2 expressing HEK293 dual reporter cells (NF-κB pathway) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkd-htlr2ni
|
|
||
|
HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkd-htlr2ni-av
|
Notification: Reference #hkd-htlr2ni-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkd-htlr2ni.
NF-κB–SEAP and IL-8–Lucia reporter HEK293 cells expressing human TLR2
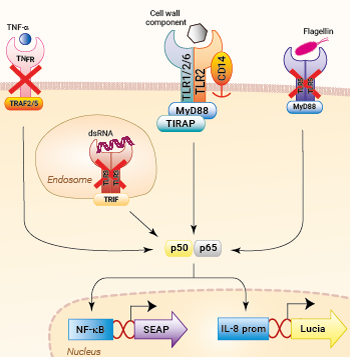
Signaling pathways in HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 cells
InvivoGen offers a human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293)-derived cell line, specifically designed to assess the distinct role of the human Toll-like receptor 2 (hTLR2):
— HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 cells*
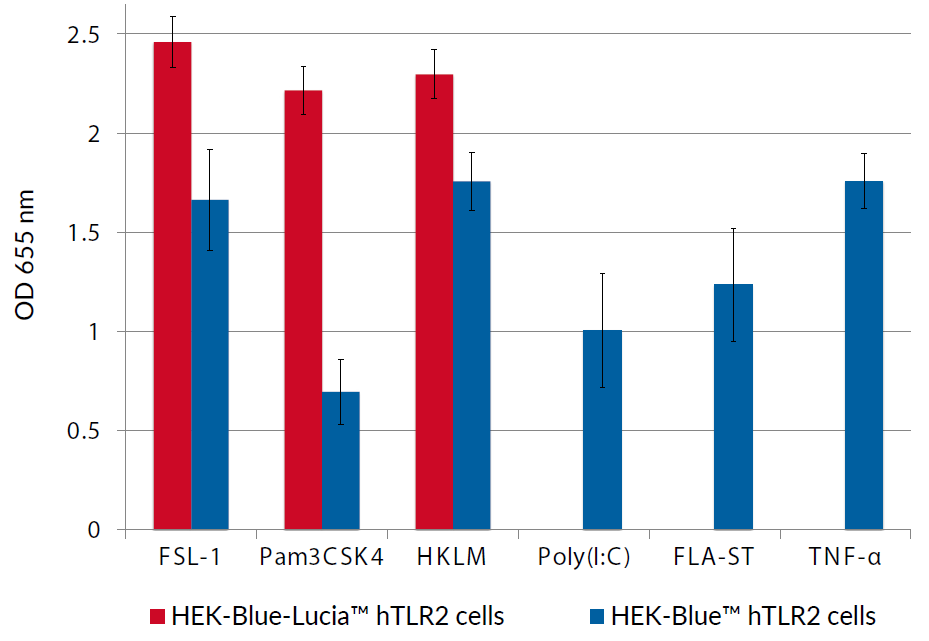
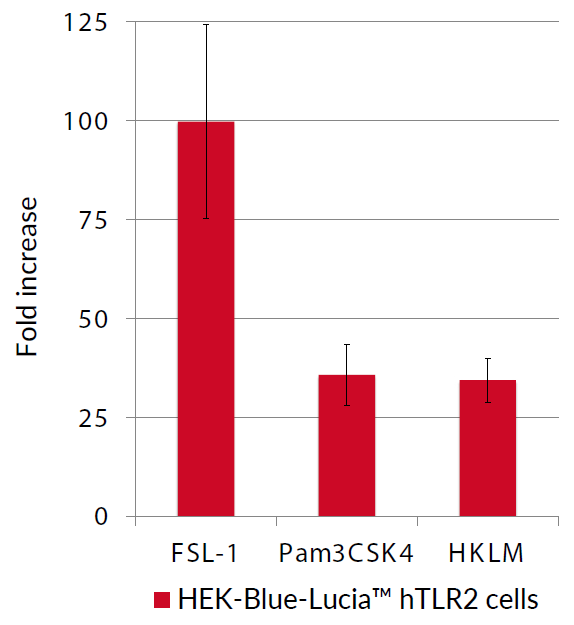
These cells were generated from the HEK-Blue-Lucia™ Null cell line harboring two inducible reporter genes. This feature allows the double readout of the NF-κB/AP-1 pathway, by monitoring the SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) or Lucia luciferase activities. HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 cells also stably express the hTLR2 and CD14 genes. Due to a triple knockout (KO) of TLR3, TLR5, and TNFR, this cell line allows for the independent study of TLR2.
Stimulation of HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 cells with TLR2 agonists (e.g. Pam3CSK4) triggers the activation of the artificial NF-κB-inducible promoter and the subsequent production of SEAP. It also promotes the expression of Lucia luciferase, which is knocked in (KI) downstream of the endogenous (more physiological) IL-8 promoter (see figures).
IL-8 (interleukin 8) is a chemokine produced in response to TLR agonists in an NF-κB/AP-1-dependent manner [1-2]. This feature enables the double readout study of the NF-κB/AP-1 pathway, by monitoring the activity of SEAP and Lucia luciferase using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution (SEAP detection reagent) or QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia (luciferase detection reagent), respectively. Thus, you may choose the readout depending on your laboratory equipment utilizing a spectrophotometer for SEAP or a luminometer for Lucia luciferase detection.
TLR2 is an important pattern recognition receptor (PRR) detecting a large spectrum of microbial pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as fungi, parasites, and viruses [3].
Key features:
- Stable overexpression of hTLR2 and CD14
- Verified KO for the TLR3, TLR5, and TNFR genes
- Functionally validated using a selection of PRR ligands and cytokines
- Readily assessable NF-κB activation by assessing the SEAP and/or Lucia luciferase activities
Applications:
- Defining the role of TLR2-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway
- Screening for novel TLR2 agonists and inhibitors
- Choice of readout depending on the laboratory equipment (spectrophotometer for SEAP or luminometer for Lucia luciferase detection).
*Note: This cell line has been renamed. It was formerly known as "HEK-Dual™ hTLR2 (NF/IL8)". The cat. code (hkd-htlr2ni) remains unchanged.
References:
1. Roebuck KA. 1999. Regulation of interleukin-8 gene expression. J Interferon Cytokine Res:429-38.
2. Ohta K, et al. 2014. Toll-like receptor (TLR) expression and TLR‑mediated interleukin-8 production by human submandibular gland epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. (5):2377-82.
3. Oliveira-Nascimento, L. et al. 2012. The Role of TLR2 in Infection and Immunity. Front Immunol 3, 79.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Hygromycin, Zeocin®
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 100 μg/ml Normocin™
Quality Control:
- Human TLR2 and CD14 overexpression has been verified by flow cytometry and functional assays.
- The triple KO of TLR3, TLR5, and TNFR has been verified by DNA sequencing, PCR, and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Note: HEK-Blue-Lucia™ hTLR2 cells are resistant to Blasticidin, Hygromycin, and Zeocin®. They should be maintained in growth medium supplemented with Hygromycin and Zeocin®.
Back to the topContents
- 3-7 x 106 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask.
- 1 ml of Hygromycin B Gold (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Details
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) plays an essential role in detecting a diverse range of microbial pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as fungi, parasites, and viruses. These PAMPs include cell-wall components such as lipoproteins, lipoteichoic acid (LTA; Gram-positive bacteria only), lipoarabinomannan (mycobacteria only), and zymosan (yeast) [1]. TLR2 forms a heterodimer on the cell surface, crucial for signaling and ligand specificity, with co-receptors TLR1 or TLR6. For example, TLR2-TLR1 and TLR2-TLR6 heterodimers are known to bind specific lipoproteins depending on whether they are tri- or diacylated, respectively [2, 3]. Moreover, ligand recognition is enhanced by its non-specific delivery to TLR2 by CD14, and sometimes in combination with additional ligand-specific molecules such as CD36 and Dectin-1 [4, 5].
Upon ligand recognition, TLR2-dependent signaling cascades ultimately lead to a MyD88 and MAL/TIRAP-dependent activation of pro-inflammatory transcription factors such as NF-κB and AP-1 [6]. Additionally, the PI3K/Akt pathway may also be activated leading to the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines [7]. Interestingly, microarray data generated by InvivoGen clearly highlights that downstream effects differ depending on whether it’s the TLR2-TLR1 or TLR2-TLR6 heterodimer that is activated upon ligand recognition.
References:
1. Oliveira-Nascimento, L. et al. 2012. The Role of TLR2 in Infection and Immunity. Front Immunol 3, 79.
2. Takeuchi, O. et al. 2001. Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol 13, 933-940.
3. Takeuchi, O. et al. 2002. Cutting edge: role of Toll-like receptor 1 in mediating immune response to microbial lipoproteins. J Immunol 169, 10-14.
4. Jimenez-Dalmaroni, M.J. et al. 2009. Soluble CD36 ectodomain binds negatively charged diacylglycerol ligands and acts as a co-receptor for TLR2. PLoS One 4, e7411.
5. Lotz, S. et al. 2004. Highly purified lipoteichoic acid activates neutrophil granulocytes and delays their spontaneous apoptosis via CD14 and TLR2. J Leukoc Biol 75, 467-477.
6. Piao, W. et al. 2016. Differential adapter recruitment by TLR2 co-receptors. Pathog Dis 74.
7. Santos-Sierra, S. et al. 2009. Mal connects TLR2 to PI3Kinase activation and phagocyte polarization. EMBO J 28, 2018-2027.