Human TLR9 Reporter HEK293 Cells (NF-κB and IRF)
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Dual™ hTLR9 Cells Human TLR9 expressing HEK293 dual reporter cells (NF-κB and IRF pathways) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkd-htlr9
|
|
||
|
HEK-Dual™ hTLR9 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkd-htlr9-av
|
--- |
Notification: Reference #hkd-htlr9-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkd-htlr9.
NF-κB–SEAP and IRF–Lucia reporter HEK293 cells expressing human TLR9
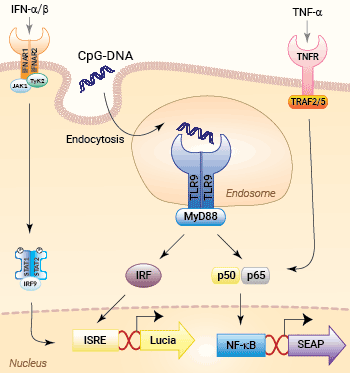
Signaling pathways in HEK-Dual™ hTLR9 cells
HEK-Dual™ hTLR9 cells were were engineered from HEK-Dual™ cells, a human embryonic kidney HEK293-derived cell line, to study the Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9)-dependent NF-κB and IRF pathway. This important pattern recognition receptor (PRR) recognizes unmethylated CpG dinucleotides, a hallmark of microbial or host-derived self DNA, and subsequently triggers NF-κB and IRF immune responses [1].
Description
HEK-Dual™ hTLR9 cells feature the stable expression of the human TLR9 gene as well as two inducible reporter genes for SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) and Lucia luciferase. As a result, these cells allow the simultaneous study of the NF-κB pathway, by monitoring the activity of SEAP, and the IRF pathway, by assessing the activity of the secreted Lucia luciferase. Upon TLR9 activation, both reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent, and QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent.
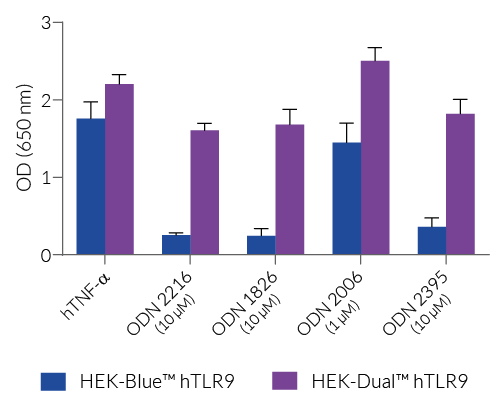
HEK-Dual™ hTLR9 cells are highly responsive to TLR9 agonists, such as oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs). They show potent NF-κB and IRF responses upon incubation of CpG-ODNs of class A (e.g. ODN 2216), class B (e.g. ODN 2006), and class C (e.g. ODN 2395), when compared to their parental cell line HEK-Dual™ (see figures).
Of note, HEK293 cells express endogenous levels of various PRRs, including TLR3, TLR5, and RIG-I-like receptors, and therefore might respond to their cognate ligands.
Key features
- Stable expression of human TLR9
- Strong response to synthetic DNA containing CpG motifs
- Distinct monitoring of TLR9-dependent NF-κB or IRF activation by assessing the SEAP and Lucia luciferase activities
Applications
- Defining the role of TLR9-dependent IRF and NF-κB signaling pathways
- Screening for novel TLR9 agonists and inhibitors in comparison with their parental cell line HEK-Dual™
1. Kumagai Y. et al., 2008. TLR9 as a key receptor of the recognition of DNA. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 60(7):795-804.
Back to the topSpecifications
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Hygromycin B, Puromycin, Zeocin®
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 100 μg/ml Normocin™
Quality Control:
- Stable expression of human TLR9 has been verified by RT-qPCR and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
- 1 ml Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Hygromycin B Gold (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Puromycin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
Toll-Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) is an endosomal receptor that triggers NF-κB- and IRF-mediated pro-inflammatory responses upon the recognition of unmethylated cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanosine (CpG) forms of DNA [1-3]. Unmethylated CpG dinucleotides are a hallmark of microbial (bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasite) DNA, as well as mitochondrial self-DNA [3,4]. These TLR9 agonists can be mimicked by synthetic oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs), which have been extensively studied to improve adaptive immune responses in the context of vaccination [1,3].
TLR9 is mainly expressed in subsets of Dendritic Cells and in B cells of all mammals. In rodents, but not in humans, TLR9 is also expressed in monocytes and macrophages [3]. The structure of the receptor varies by 24% between human TLR9 (hTLR9) and mouse TLR9 (mTLR9) [3]. They recognize different CpG motifs, the optimal sequences being GTCGTT and GACGTT for hTLR9 and mTLR9, respectively [5].
![]() Get more information about CpG-ODNs Classes.
Get more information about CpG-ODNs Classes.
References
1. Kumagai Y. et al., 2008. TLR9 as a key receptor of the recognition of DNA. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 60(7):795-804.
2. Heinz L.X. et al., 2021. TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9. Nature. 581(7808):316-322.
3. Kayraklioglu N. et al., 2021. CpG oligonucleotides as vaccine adjuvants. DNA Vaccines: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 2197. p51-77.
4. Kumar V., 2021. The trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs: guardians of the cellular galaxy against host-derived self-DNA. Front. Immunol. 11:624597.
5. Bauer S. et al., 2001. Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98(16):9237-42.