Recombinant human IL-12 protein - Bioactive cytokine
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Recombinant human IL-12 Recombinant Cytokine, source: CHO |
Show product |
10 µg 5 x 10 µg |
rcyc-hil12
|
|
Human IL-12 (linked heterodimer) protein - Mammalian cell-expressed, tag-free, with HSA
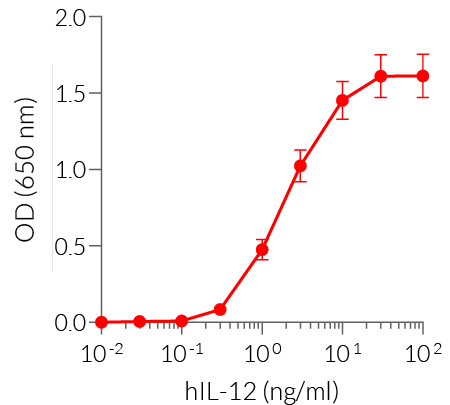
Recombinant human IL-12 (IL-12 p70) is a high-quality and biologically active cytokine, validated using proprietary IL-12 reporter cells. This pro-inflammatory cytokine is composed of two subunits, IL-12p35 and IL-12p40. It is produced in CHO cells to ensure protein glycosylation and bona fide 3D structure.
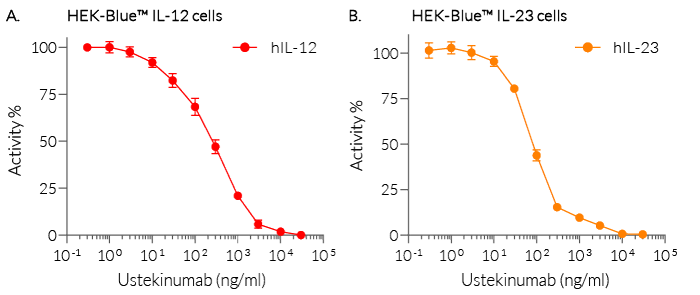
Recombinant human IL-12 can be used together with HEK-Blue™ IL-12 cells for the screening of inhibitory molecules, such as Ustekinumab, a therapeutic monoclonal antibody targeting the IL-12 p40 subunit (see figures).
IL-12 signaling and biological functions
InvivoGen also offers:
• HEK-Blue™ IL-12 cells
• Anti-IL-12/IL-23 (Ustekinumab biosimilar)
Key features
- Each lot is validated using HEK-Blue™ IL-12 cells
- Endotoxin ≤ 0.1 EU/µg
- 0.2 µm sterile-filtered
Applications
- IL-12 detection and quantification assays (positive control)
- Screening and release assays for antibodies blocking IL-12 signaling
- Screening and release assays for engineered IL-12 proteins
Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is a pleiotropic cytokine driving IFN-γ production, proliferation of activated T and NK cells, and differentiation in Th1 cells in response to microbial infections. Dysregulated IL-12 production is linked to immune-mediated inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
All InvivoGen products are for internal research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
Back to the topSpecifications
Source: Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells
Species: Human
Alternative name: IL-12 p70, Cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor (CLMF), NK cell stimulatory factor (NKSF)
Carrier: HSA (human serum albumin)
Tag: Tag-free
Construction: Heterodimer linked by 10 amino acids (a.a.)
Accession number: P29460.1 (IL-12p40), P29459.2 (IL-12p35)
Protein size: 513 a.a. (I23-S328(p40)-Linker-R23-S219(p35))
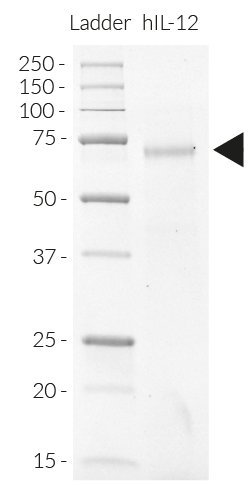
Molecular weight: ~ 70 kDa (SDS-PAGE)
Solubility: 100 μg/ml in water
Formulation: Phosphate buffer saline (pH 7.4), 5% saccharose, 1% HSA
Sterility: 0.2 µm filtration
Form: Lyophilized
Reconstitution buffer: Endotoxin-free water (provided)
Purity: ≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Endotoxin: The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Tested applications: Cellular assays
Quality control: Each lot is functionally tested and validated
Back to the topContents
Recombinant human IL-12 is provided lyophilized and is available in two quantities:
- rcyc-hil12: 10 µg
- rcyc-hil12-5: 5 x 10 µg
- 1.5 ml endotoxin-free water for rcyc-hil12 and rcyc-hil12-5
![]() Recombinant IL-12 is shipped at room temperature.
Recombinant IL-12 is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, the product should be stored at -20°C.
Upon receipt, the product should be stored at -20°C.
![]() Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Details
IL-12 background
Interleukin 12 (IL-12), also known as IL-12p70, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor (CLMF), or natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF) is the founding member of the heterodimeric IL-12 cytokine family. This family is characterized by the sharing of p19, p28, p35, p40, and Ebi3 subunits, and includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, IL-35, and IL-39 [1, 2]. The secretion of bioactive IL-12 requires the co-expression of IL-12p35 and IL-12p40 and disulfide bond formation. IL-12 is primarily produced by pathogen-activated macrophages and dendritic cells (DC) [1, 2].
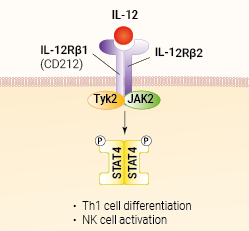
The binding of IL-12 to its IL-12Rβ1/IL-12Rβ2 heterodimeric receptor triggers a JAK2/TYK2 signal transduction leading to the activation of STAT4. Activated STAT4 forms homodimers that are translocated to the nucleus where they regulate the expression of target genes. Subsequent gene expression promotes the cytotoxic activity of Natural Killer (NK) and CD8+ T cells, and drives IFN-γ production by NK and activated CD4+ T cells [1, 2]. IFN-γ contributes to the differentiation of Th1 cells and inhibits Th2 cell development. Moreover, it enhances DC maturation and antigen presentation.
Interestingly, secreted IL-12p40 monomers and homodimers (IL-12p80) have also been found and described to function as IL-12 antagonists or agonists, depending on the experimental studies [2].
Relevance for therapeutics development
IL-12 is a key cytokine for controlling intracellular infections. However, excessive IL-12 production contributes to several immune-mediated inflammation diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, type I diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn's disease [1].
Ustekinumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (mAb) that targets the p40 subunit common to IL-12 and IL-23, preventing their interactions with their receptor common chain IL-12Rβ1 [3]. This antibody is FDA-approved for treating psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis [4]. Addressing the benefits of neutralizing IL-12 and IL-23 together or individually, depending on the clinical context can be achieved using neutralizing mAbs targeting the p19 subunit of IL-23 [5].
As IL-12 drives strong pro-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities, a series of IL-12-based products have been explored for cancer therapy. These strategies must control targeted delivery to achieve high local IL-12 while avoiding systemic toxicity [6-8].
References:
1. Dembic., Z., 2015. Chapter 6 - Cytokines of the immune system: Interleukins. The cytokines of the immune system (book): 143-239.
2. Floss, D.M., et al., 2020. IL-12 and IL-23-Close Relatives with Structural Homologies but Distinct Immunological Functions. Cells, 9(10): 2184.
3. Benson, J.M, et al., 2011. Discovery and mechanism of ustekinumab: a human monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-12 and interleukin-23 for treatment of immune-mediated disorders. MAbs 3(6):535-545.
4. FDA website accessed in Nov 2024: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2024/761044s013lbl.pdf#page=37
5. Tait Wojno, E.D. et al., 2019. The Immunobiology of the Interleukin-12 Family: Room for Discovery. Immunity. 50(4):851-870.
6. Leonard, W.J. & Lin, J. X., 2023. Strategies to therapeutically modulate cytokine action. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 22(10):827-584.
7. Briukhovetska D., et al., 2021. Interleukins in cancer: from biology to therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 21(8):481-499.
8. Yi, M., et al., 2024. Targeting cytokine and chemokine signaling pâthways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 9(1):176.
Back to the top