Jurkat-Dual™ Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Jurkat-Dual™ Cells Human T Lymphocytes - NF-κB/IRF reporter cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
jktd-isnf
|
|
||
|
Jurkat-Dual™ vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
jktd-isnf-av
|
Notification: Reference #jktd-isnf-av can only be ordered together with reference #jktd-isnf.
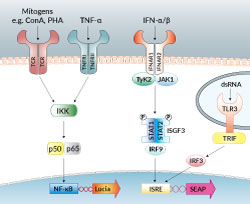
NF-κB & IRF signaling in Jurkat-Dual™ cells
IRF-SEAP & NF-κB-Luc Reporter T Lymphocytes
Jurkat-Dual™ cells are engineered reporter T lymphocytes designed for the study of transcription factor activation in a physiologically-relevant cell line. These cells stably express two inducible reporter constructs; interferon regulatory factor-inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (IRF-SEAP) and NF-κB-Lucia luciferase (NF-κB-Luc) reporter genes. They were derived from the human T lymphocyte-based Jurkat cell line.
Cell line description:
Jurkat-Dual™ cells feature the Lucia luciferase gene, a secreted luciferase reporter gene, driven by an interferon-β (IFN-β) minimal promoter fused to five copies of the NF-κB consensus transcriptional response element and three copies of the c-Rel binding site. These cells also express a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene under the control of an IFN-stimulated gene 54 (ISG54) minimal promoter in conjunction with five IFN-stimulated response elements. As a result, Jurkat-Dual™ cells allow the simultaneous study of the NF-κB pathway, by monitoring the activity of Lucia luciferase, and the IRF pathway, by assessing the activity of SEAP. Both reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia and Gaussia luciferase detection reagent, and QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
Jurkat-Dual™ cells induce the activation of NF-κB in response to TNF-α and T-Lymphocyte mitogens, such as phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A. They trigger the IRF pathway upon stimulation with type I IFNs and poly(I:C).
Features of Jurkat-Dual™ cells:
- Readily assessable SEAP and Lucia luciferase reporter activity
- The stability for 20 passages has been verified
- Functionally tested and guaranteed mycoplasma-free
Application of Jurkat-Dual™ cells:
- Monitoring IRF and NF-κB activation in T lymphocytes
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®, blasticidin
Growth medium: IMDM, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; 30 min at 56 °C), 100 μg/ml Pen-Strep (100 U/ml-100 μg/ml), Normocin™
Quality control:
- Reporter activity has been validated using functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages following thawing has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 1 vial of Jurkat-Dual™ cells (3-7 x 106 cells)
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
The human Jurkat cell line was established from acute T cell leukemia. Jurkat cells have been extensively used in vitro to delineate the signaling pathways induced by the engagement of T-cell receptors and to study the expression of various chemokine receptors susceptible to viral entry, particularly HIV [1]. T cell activation results in the nuclear translocation of transcription factors, such as IRFs (interferon regulatory factors) and NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) to induce the expression of target genes. Knowledge of their signaling cascades, ease of culture, and transfection make Jurkat cells a convenient tool to screen for T-cell activation, anti-viral or anti-cancer drugs.
References:
1. Montano M. 2014. Model systems. Translational Biology in Medicine. 9-33.
Back to the top





