Jurkat ICOS/ICOS-L assay
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Jurkat-Lucia™ hICOS Cells NFAT-Luc Reporter T Lymphocytes expressing human ICOS |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
jktl-icos
|
|
||
|
Jurkat-Lucia™ hICOS vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
jktl-icos-av
|
Notification:
Reference #jktl-icos-av can only be ordered together with reference #jktl-icos.
Agonist screening assay for ICOS/ICOS-L axis
InvivoGen offers a cellular assay specifically designed for screening antibody-, Fc-fusion protein-, or small-molecule agonists of the ICOS/ICOS-L immune checkpoint (IC) axis:
- Jurkat-Lucia™ hICOS: Reporter T cells
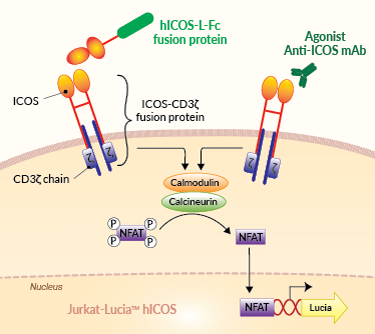
Principle of ICOS cellular assay
(click to enlarge)
 InvivoGen also offers:
InvivoGen also offers:
• Antagonist screening assay for ICOS/ICOS-L axis
• hICOS-L-Fc fusion protein
• hICOS-Fc fusion protein
Inducible Co-stimulator (ICOS, CD278) is an immunostimulatory IC and a member of the CD28 superfamily. Expression of ICOS is rapidly induced in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells upon their activation, whereas its ligand ICOS-L (also known as CD275), is mostly expressed by antigen-presenting cells [1].
Assay principle:
This assay relies on the monitored activation of Jurkat-Lucia™-ICOS cells which express a hICOS-CD3ζ fusion protein along with the Lucia luciferase reporter gene under the control of an ISG54 minimal promoter fused to six NFAT response elements. CD3ζ is a key component of the T-cell receptor (TCR) and CD3 complex that triggers TCR downstream signaling.
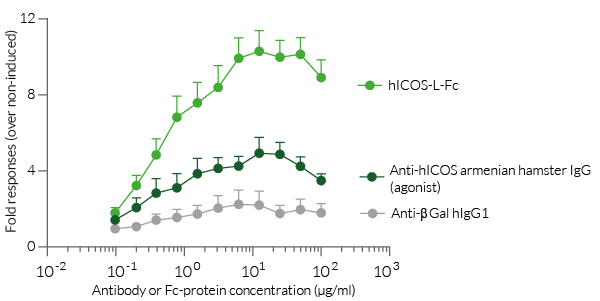
In the presence of a potent ICOS agonist, such as hICOS-L-Fc, hICOS-CD3ζ triggers NFAT activation and Lucia production. Activation of the reporter T cells can be readily measured using QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia detection reagent (see Figures).
T-cell key features:
- Stable hICOS-CD3ζ expression
- NFAT-inducible Lucia luciferase reporter activity
InvivoGen also offers Jurkat-Raji ICOS/ICOS-L (Bio-IC™), a cellular assay for screening antagonists of the ICOS/ICOS-L axis.
![]() Read our review on Immune Checkpoint Blockade
Read our review on Immune Checkpoint Blockade
![]() Learn more about Immune Checkpoint Antibodies.
Learn more about Immune Checkpoint Antibodies.
Reference:
1. Amatore, F. et al. 2020. Role of ICOS in cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 20, 141-150.
Back to the topSpecifications
Growth medium: IMDM, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin and Zeocin®
Quality Control:
- Human ICOS surface expression is confirmed by flow cytometry.
- Reporter activity is validated following co-culture with Raji-hICOS-L cells.
- The stability for 20 passages following thawing is verified.
- The cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 Jurkat-Lucia™ -hICOS cells
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada)
Details
Inducible Co-stimulator (ICOS, CD278) is an immunostimulatory IC and a member of the CD28 superfamily. Expression of ICOS is rapidly induced in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells upon their activation, whereas its ligand ICOS-L (also known as CD275), is mostly expressed by antigen-presenting cells [1]. The interaction between ICOS and ICOS-L delivers a secondary co-stimulatory signal through the activation of the transcription factor AKT, which promotes T cell proliferation and differentiation as well as the production of cytokines [1]. In tumor immunity, ICOS is involved in the amplification of the anti-tumor cytotoxic CD8+ T cell response, as well as the 'pro-tumor' function and maintenance of regulatory T cells (Tregs). Therefore, both agonistic and antagonistic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting this pathway are being investigated in combinational cancer immunotherapy [2]. Notably, ICOS agonistic mAbs have been shown to potentiate the effects of anti-CTLA-4 mAbs [3].
References:
1. Amatore, F. et al. 2020. Role of ICOS in cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 20, 141-150.
2. Solinas, C. et al. 2020. The rationale behind targeting the ICOS-ICOS ligand costimulatory pathway in cancer immunotherapy. ESMO Open 5.
3. Soldevilla, M.M. et al. 2019. ICOS Costimulation at the Tumor Site in Combination with CTLA-4 Blockade Therapy Elicits Strong Tumor Immunity. Mol Ther 27, 1878-1891.