Human TLR9 Reporter THP-1 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 Cells Human TLR9 Overexpressing - THP-1 Reporter Monocytes |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-htlr9
|
|
||
|
THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-htlr9-av
|
Notification: Reference #thpd-htlr9-av can only be ordered together with reference #thpd-htlr9.
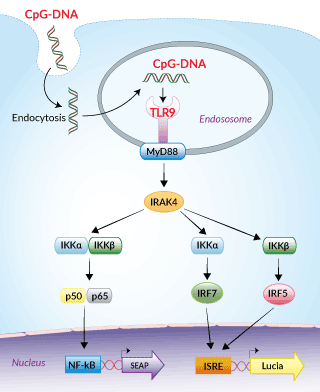
Reporter systems in THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 cells
Dual reporter monocytes for TLR9 pathway studies
InvivoGen offers a human monocyte-derived cell line, specifically designed for the study of human TLR9 (Toll-Like Receptor 9) signaling pathways:
• THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 cells
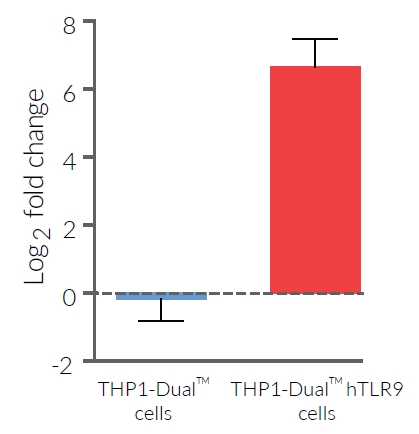
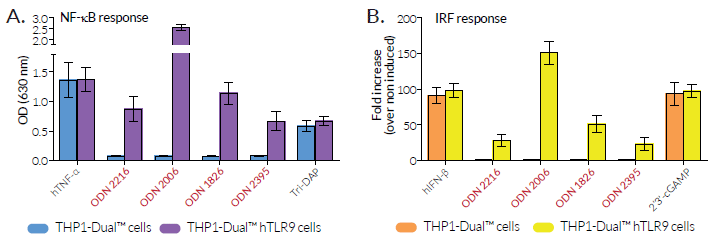
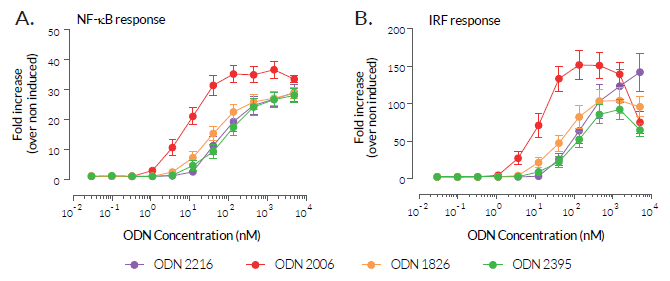
THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 cells overexpress the human TLR9 (hTLR9) gene. They also feature two inducible reporter genes, allowing the concomitant study of the IRF and NF-κB pathways, by monitoring the Lucia luciferase and SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) activities, respectively.
Unlike their parental cells, THP1-Dual™, which weakly express TLR9, THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 cells are responsive to stimulation with TLR9 agonists, such as oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs). As expected, hTLR9 overexpression in THP1-Dual™ cells allows potent NF-κB and IRF responses upon incubation with CpG-ODNs of class A (ODN 2216), class B (ODN 2006, ODN 1826), and class C (ODN 2395). Of note, THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 cells are more responsive to the class B, human-preferred, ODN 2006 (see Figures).
Background:
Toll-Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) is one of the most studied pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) for nucleic acids. It is an endosomal receptor that triggers NF-κB- and IRF-mediated pro-inflammatory responses upon the recognition of unmethylated cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanosine (CpG) forms of DNA [1-3]. TLR9 agonists can be mimicked by synthetic oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs) [1,3].
Key features:
- Verified overexpression of TLR9 gene by qRT-PCR
- Functionally validated with a selection of TLR9 agonists
- Readily assessable Lucia luciferase and SEAP reporter activities
Applications:
- Study of IRF and NF-κB-dependent TLR9 signaling pathways
- Screening of novel specific activators or inhibitors of the TLR9 signaling pathways
References
1. Kumagai Y. et al., 2008. TLR9 as a key receptor of the recognition of DNA. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 60(7):795-804.
2. Heinz L.X. et al., 2021. TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9. Nature. 581(7808):316-322.
3. Kayraklioglu N. et al., 2021. CpG oligonucleotides as vaccine adjuvants. DNA Vaccines: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 2197. p51-77.
Specifications
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Zeocin®, and Puromycin
Quality Control:
- Human TLR9 expression has been verified by qRT-PCR and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 THP1-Dual™ hTLR9 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Puromycin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
Toll-Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) is an endosomal receptor that triggers NF-κB- and IRF-mediated pro-inflammatory responses upon the recognition of unmethylated cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanosine (CpG) forms of DNA [1-3]. Unmethylated CpG dinucleotides are a hallmark of microbial (bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasite) DNA, as well as mitochondrial self-DNA [3,4]. These TLR9 agonists can be mimicked by synthetic oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs), which have been extensively studied to improve adaptive immune responses in the context of vaccination [1,3].
TLR9 is mainly expressed in subsets of Dendritic Cells and in B cells of all mammals. In rodents, but not in humans, TLR9 is also expressed in monocytes and macrophages [3]. The structure of the receptor varies by 24% between human TLR9 (hTLR9) and mouse TLR9 (mTLR9) [3]. They recognize different CpG motifs, the optimal sequences being GTCGTT and GACGTT for hTLR9 and mTLR9, respectively [5].
![]() Get more information about CpG-ODNs Classes.
Get more information about CpG-ODNs Classes.
References
1. Kumagai Y. et al., 2008. TLR9 as a key receptor of the recognition of DNA. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 60(7):795-804.
2. Heinz L.X. et al., 2021. TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9. Nature. 581(7808):316-322.
3. Kayraklioglu N. et al., 2021. CpG oligonucleotides as vaccine adjuvants. DNA Vaccines: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 2197. p51-77.
4. Kumar V., 2021. The trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs: guardians of the cellular galaxy against host-derived self-DNA. Front. Immunol. 11:624597.
5. Bauer S. et al., 2001. Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98(16):9237-42.