THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-Dual KO-cGAS Cells Human THP-1 Monocytes - cGAS knockout NF-κB-SEAP and IRF-Lucia Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-kocgas
|
|
||
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-kocgas-av
|
Notification: Reference #thpd-kocgas-av can only be ordered together with reference #thpd-kocgas.
cGAS knockout NF-κB-SEAP and IRF-Lucia luciferase reporter monocytes
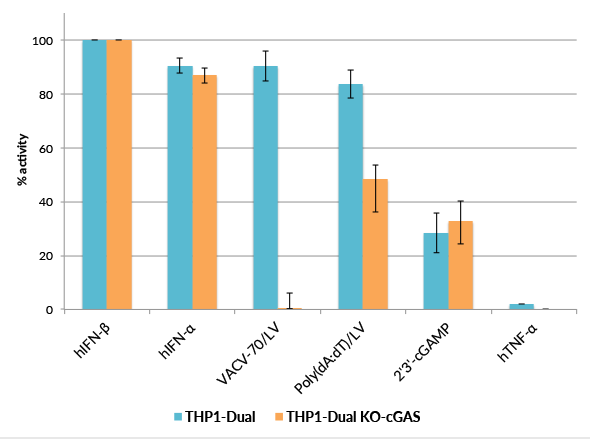
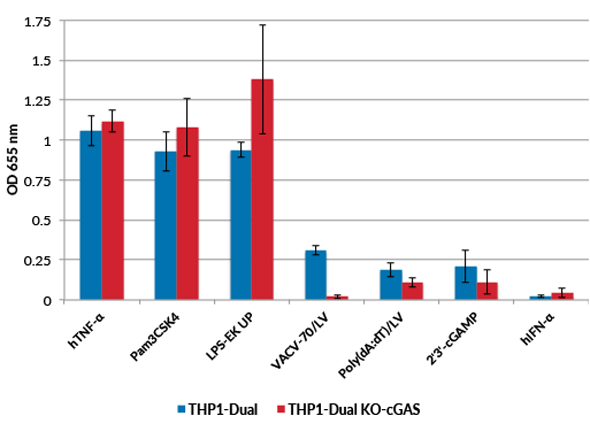
THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS cells were generated from THP1-Dual™ cells by stable knockout of the cGAS gene. They derive from human THP-1 monocytes, a cell line often used to study DNA sensing pathways as they express all the cytosolic DNA sensors identified so far (with the exception of DAI).
THP1-Dual™ and THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS cells stably express two inducible secreted reporter genes: Lucia luciferase and SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase). The Lucia luciferase reporter gene is under the control of an ISG54 (interferon-stimulated gene) minimal promoter in conjunction with five IFN-stimulated response elements. The SEAP gene is driven by an IFN-β minimal promoter fused to five copies of the NF-kB response element. As a result, they allow the simultaneous study of the IFN regulatory factor (IRF) and the NF-kB pathway by assessing the activity of Lucia luciferase and SEAP, respectively. Both reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia and Gaussia luciferase detection reagent, and QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS and THP1-Dual™ cells can be used to study the role of cGAS by monitoring IRF-induced Lucia luciferase activity. THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS cells are resistant to blasticidin and Zeocin®.
References:
1. Sun L. et al., 2013. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339(6121):786-91.
2. Gao P. et al., 2013. Cyclic [G(2’,5’)pA(3’,5’)p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. Cell. 153(5):1094-107.
3. Ablasser A. et al., 2013. cGAS produces a 2’-5’-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING. Nature. 498(7454):380-4.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®, blasticidin
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 μg/ml Normocin™, Pen-Strep (100 U/ml-100 μg/ml)
Quality control
Biallelic cGAS knockout is verified by functional assays, PCR, and DNA sequencing.
These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 1 vial of THP1-Dual™ KO-cGAS cells (3-7 x 106 cells) in freezing medium
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria and fungi.
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
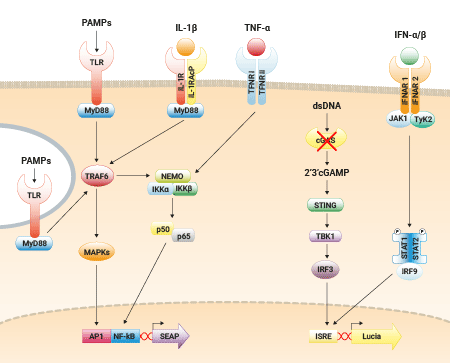
THP1 reporter cells are a family of cells derived from the human monocytic THP-1 cell line, which naturally expresses many pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs), including Toll-like receptors.
They respond to ligands for certain TLRs; namely, TLR2, TLR1/2, TLR2/6, TLR4, TLR5 and TLR8. These cells can also be used to study DNA sensing pathways, as they are highly responsive to PRR agonists that trigger interferon (IFN) signaling pathways.
THP1‑Dual™ cells feature two reporter genes that enable the simultaneous study of the NF-κB and IFN signaling pathways.
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS, cGAMP synthase) is a critical cytosolic DNA sensor that triggers innate immune responses through the production of type I interferons (IFNs) [1]. In response to cytosolic double‑stranded DNA (dsDNA), cGAS produces the cyclic dinucleotide (CDN) 2’3’-cGAMP. CDNs bind directly to STING, leading to TBK1‑IRF3-mediated activation of IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) in the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG). The most potent agonist of human STING is 2’3’-cGAMP [2,3].
Back to the top