ASC expressing RAW 264.7 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RAW-ASC Cells ASC expressing RAW 264.7 cells (murine macrophages) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
raw-asc
|
|
||
|
RAW-ASC vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
raw-asc-av
|
Notification: Reference #raw-asc-av can only be ordered together with reference #raw-asc.
ASC expressing RAW 264.7 cells
The role of ASC in canonical inflammasomes
ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD domain, also known as PYCARD) is a protein adaptor important in canonical inflammasome responses [1].
To foster studies on the ASC adaptor, InvivoGen has developed RAW-ASC cells, which were generated by stable transfection of the murine ASC gene into the murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line, which is naturally ASC-deficient [2].
• RAW-ASC cells – Murine ASC gene expression
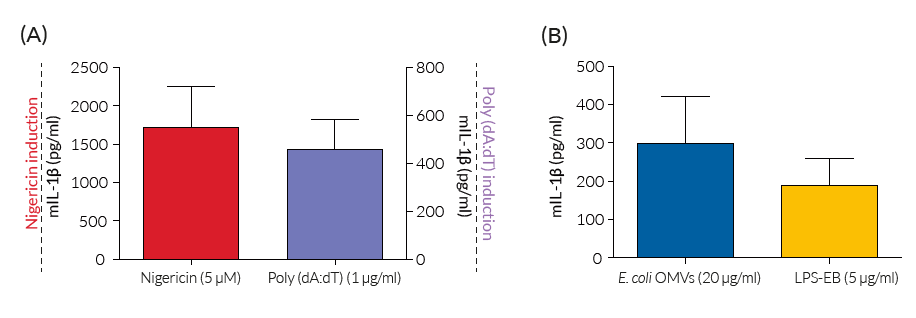
In contrast to the parental cell line, RAW-ASC cells produce and secrete mature IL-1β upon activation of the canonical inflammasome sensors NLRP3 (using Nigericin) and AIM2 (using Poly(dA:dT)), as well as upon activation of the non-canonical inflammasome (using LPS or E. coli outer membrane vesicles). This cell line is a useful tool to study the role of ASC in inflammasome responses and is an alternative to the in vitro differentiation of mouse bone-marrow-derived macrophages. Additionally, it is the parental and control cell line of InvivoGen's RAW-ASC KO-GSDMD cells, for which all inflammasome responses are abrogated.
FEATURES OF RAW-ASC CELLS:
- Verified expression of the murine ASC gene by Western Blot (Wes™)
- Validated secretion of mature IL-1β and pyroptosis after canonical and non-canonical inflammasome activation
- Parental cell line for RAW-ASC KO-GSDMD cells and RAW-ASC KO-CASP11 cells
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
References:
1. Mathur A. et al., 2017. Molecular mechanisms of inflammasome signaling. J. Leuk. Biol. 103:233.
2. Pelerin P. et al., 2008. P2X7 receptor differentially couples to distinct release pathways for IL-1β in mouse macrophage. J. Immunol. 180:7147.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 4 mM L-glutamine, 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Test medium: DMEM without phenol red, 4.5 g/l glucose, 4 mM L-glutamine, 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin.
Note: Phenol red causes high background signal in the LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) assay used to monitor inflammasome-induced cell death.
Quality Control:
- ASC transfection has been verified by Western blot (WES™) and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 RAW-ASC cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasma, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
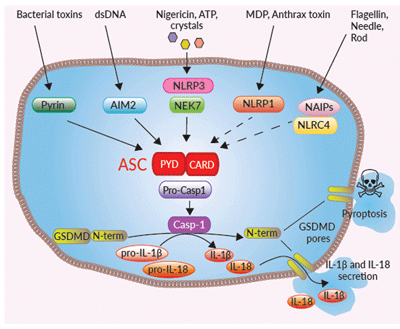
Inflammasomes are multimeric protein complexes that are crucial for host defense against infection and response to endogenous danger signals. The canonical inflammasome response is driven by aggregation of a sensor (i.e. NLRP3) with the ASC adaptor and pro-caspase-1. Activation of caspase-1 (CASP1) induces the maturation of pro-IL-1β/pro-IL-18 and cleavage of the pore-forming protein gasdermin D (GSDMD), leading to secretion of IL-1β/ 18 and pyroptosis.
ASC is essential to inflammasome sensors that do not contain a CARD domain, such as NLRP3, AIM2, and Pyrin [1]. This is due to the bipartite composition of ASC, consisting of one PYD and one CARD domain, allowing the recruitment of the CARD-containing pro-caspase-1 to these sensors. Whereas, the NLRP1 and NLRC4 inflammasome sensors have a CARD domain, and can recruit pro caspase-1 either directly or through ASC. However, it has been shown that upon activation of these sensors, in the absence of ASC, the secretion of mature IL-1β and IL-18 is reduced [1]. As the non-canonical inflammasome (i.e. CASP4/5/11) can not directly activate CASP1, they trigger GSDMD-driven release of alarmins and K+ efflux to induce the activation of NLRP3 and CASP1-mediated IL-1β/-18 maturation and secretion. Therefore, the absence of ASC affects the downstream inflammatory signaling from the non-canonical inflammasome also.
1. Mathur A. et al., 2017. Molecular mechanisms of inflammasome signaling. J. Leuk. Biol. 103:233.
Back to the top