TLR4 KO Reporter RAW 264.7 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 Cells TLR4 knockout IRF and MIP-2 (NF-κB) reporter mouse macrophages |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
rawd-kotlr4
|
|
||
|
RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
rawd-kotlr4-av
|
Notification: Reference #rawd-kotlr4-av can only be ordered together with reference #rawd-kotlr4.
TLR4 knockout IRF-Lucia & MIP-2-knockin-SEAP murine macrophage reporter cell line
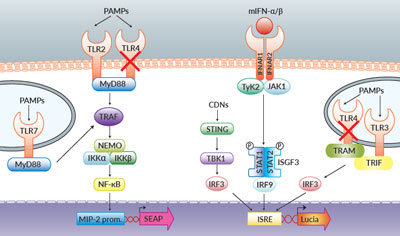
TLR and Type I IFN signaling in RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 Cells
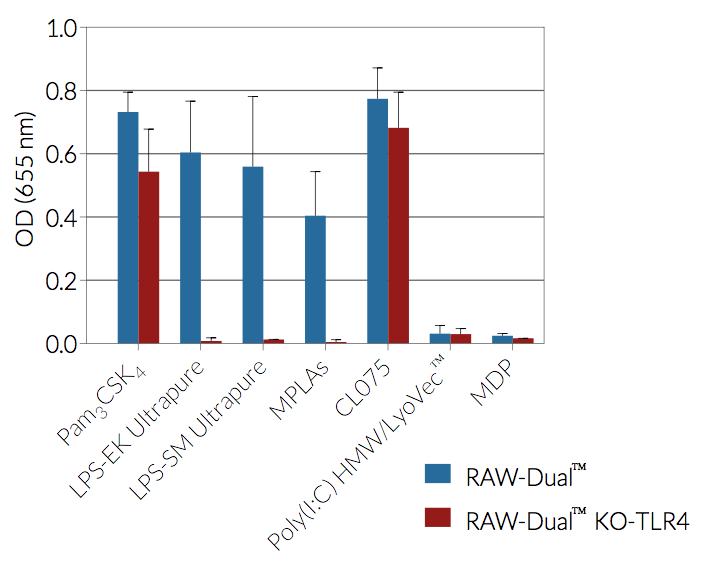
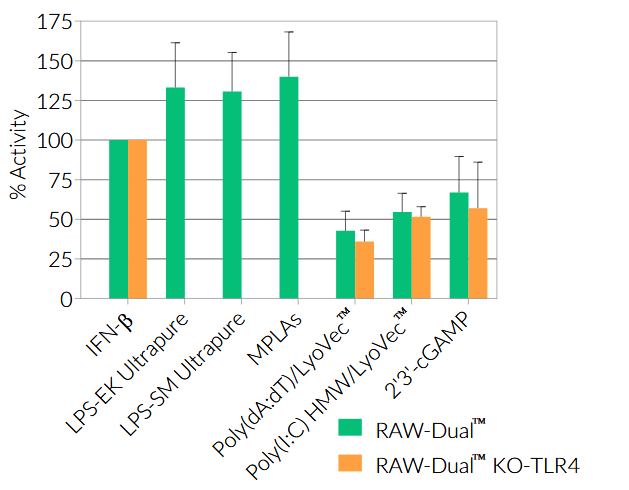
RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 (IRF-Lucia/KI-[MIP-2]SEAP) cells were generated from RAW-Dual™ cells through stable gene knockout of Toll‑like receptor 4 (TLR4). These cells derive from RAW 264.7 murine macrophages which express many pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) [1].
RAW‑Dual™ KO-TLR4, along with their parental cell line RAW-Dual™ cells, can be used to:
- Investigate TLR4 signaling
- Study TLR4-independent biological activity of test compounds.
Both cell lines stably express two reporter genes encoding SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) and Lucia luciferase.
- SEAP expression depends on the activation of the endogenous MIP-2 promoter. MIP‑2 is a chemokine produced in an NF-κB-dependent manner [2]. The MIP-2 ORF has been replaced by the SEAP ORF using knockin technology. Hence SEAP expression reports activation of NF-κB.
- The Lucia luciferase gene is under the control of an ISG54 minimal promoter in conjunction with five IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE). It reports the activation of interferon regulatory factors (IRFs).
- Both reporter proteins are secreted and readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent, and QUANTI‑Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia and Gaussia detection reagent. Alternatively, SEAP activity can be detected using HEK-Blue™ Detection, a cell culture medium allowing real-time detection of SEAP.
As a result, RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 cells allow to simultaneously study the NF-κB pathway, by assessing the activity of SEAP, and the IRF pathway, by monitoring the activity of Lucia luciferase.
As expected, RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 cells do not respond to TLR4 agonists such as whole lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or monophosphoryl lipid A (MLPA).
RAW-Dual KO-TLR4™ cells are resistant to Zeocin®.
References:
1. West A. et al., 2011.TLR signalling augments macrophage bactericidal activity through mitochondrial ROS. Nature 472:476-80.
2. Kim D. et al., 2003. NF-kappaB and c-Jun-dependent regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-2 gene expression in response to lipopolysaccharide in RAW 264.7 cells. Mol Immunol. 40:633-43.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®
Growth medium: DMEM, 2 mM L-glutamine, 4.5 g/l glucose, 10% FBS supplemented with 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Quality Control:
- Biallelic TLR4 knockout has been verified by DNA sequencing and functional assays.
- The biallelic replacement of the mouse MIP-2 (macrophage inflammatory protein-2; CXCL2; murine homolog of IL-8) open reading frame (ORF) with the SEAP reporter ORF has been verified by PCR and sequencing. Furthermore, the inability to produce MIP-2 has been confirmed by ELISA.
- Activity of RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 cells has been tested with pattern recognition receptor (PRR) ligands that trigger the NF-κB and interferon regulatory factor (IRF) signaling pathways.
- Cell line stability for 20 passages following thawing has been verified.
- RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 of RAW-Dual™ KO-TLR4 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria and fungi.
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
Toll‑like receptor 4 (TLR4) is the receptor for Gram-negative lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and its toxic moiety called lipid A. TLR4 interacts with three different extracellular proteins: the LPS-binding protein (LBP), CD14, and the myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD‑2). Their interaction induces a signaling cascade resulting in the activation of NF-κB and the production of proinflammatory cytokines. LPS contamination is a common issue arising when testing novel compounds, such as recombinant proteins, leading to unreliable results. TLR4 knockout cells ensure the study of PRR pathways without interference from LPS.
Back to the top