ATP
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ATP Adenosine 5'-triphosphate disodium salt |
Show product |
1 g |
tlrl-atpl
|
|
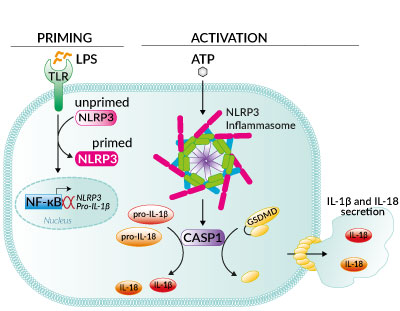
Inflammasome activation with ATP
NLRP3 Inflammasome Inducer - Adenosine 5'-triphosphate disodium salt
The organic compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a key potassium (K+) efflux agent, that induces the NLRP3 inflammasome formation by signaling through the cell surface receptor P2X7. It stimulates the caspase-1-dependent cleavage and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and IL-18 [1].
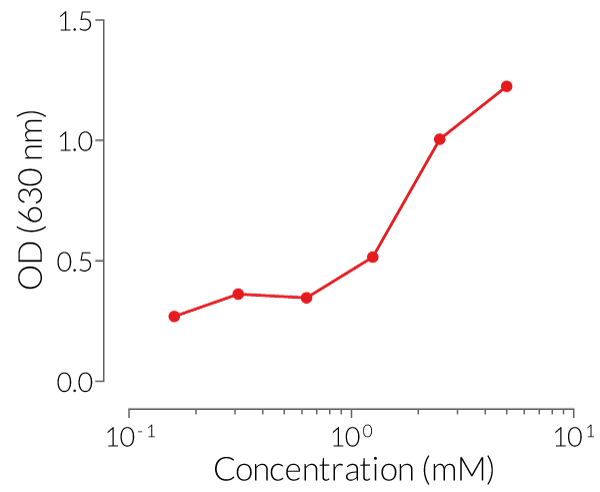
The biological activity of ATP has been validated using InvivoGen's THP-1 Null cells and HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells.
 InvivoGen also offers:
InvivoGen also offers:
• HEK-Blue™ IL-1β: IL-1β Sensor Cells
• THP1-HMGB1-Lucia™: Pyroptosis Reporter Cells
Key features:
- Inducer of the NLRP3 inflammasome
- Highly pure
- Each lot is functionally tested
![]() Read our review on the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Read our review on the NLRP3 inflammasome.
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes.
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes.
Reference:
1. Amores-Iniesta J, et al., 2017. Extracellular ATP Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Is an Early Danger Signal of Skin Allograft Rejection. Cell Rep.;21(12):3414-3426.
Back to the topSpecifications
Working concentration: 5 mM
CAS number: 987-65-5
Molecular Weight: 551.14
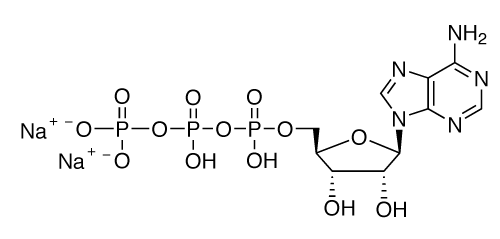
Formula: C10H14N5O13P3 .2Na
Purity: ≥99.0% (HPLC)
Solubility: 400 mg/ml (725 mM) in water
Quality control:
- The biological activity has been validated using cellular assays.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK-Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Contents
- 1g ATP (adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium salt) provided lyophilized
![]() ATP is shipped at room temperature.
ATP is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Store at -20°C.
Store at -20°C.
Details
Extracellular ATP is a key danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) that is able to acitvate the NLRP3 inflammasome. It triggers the opening of the non-selective cation channel of the purinergic P2X7 receptor, followed by the subsequent alteration of the intracellular K+ concentration [1].
The NLRP3 inflammasome is an intracellular multi-protein complex that plays a central role in innate immunity. It is activated by a two-step process. A first signal (‘priming’) is provided by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or cytokines. It allows the transcriptional upregulation of key inflammasome actors and the post-translational modification of NLRP3 . The second signal (‘activation’) is provided by a wide array of stimuli including microbial toxins, endogenous molecules or crystalline substances. The current paradigm is that NLRP3 does not bind directly to these molecules. Rather it senses downstream cytosolic stress signals such as K+ efflux. This triggers inflammasome multimerization and pro-caspase-1 maturation. Proximity-induced autolytic activation of caspase-1 leads to the formation of gasdermin D (GSDMD) pores at the cell surface, allowing IL-1β/IL-18 and alarmin secretion, and ultimately, pyroptosis [3,4].
References:
1. Amores-Iniesta J, et al., 2017. Extracellular ATP Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Is an Early Danger Signal of Skin Allograft Rejection. Cell Rep.;21(12):3414-3426.
2. Swanson K.V. et al., 2019. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19:477.
3. Groslambert M. & Py B. 2018. Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 11:359.
Chemical structure of ATP: