NLRP3 KO & KD THP-1 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-KO-NLRP3 Cells NLRP3 Knockout in THP-1 cells (human monocytes) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-konlrp3z
|
|
||
|
THP1-KO-NLRP3 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-konlrp3z-av
|
|||
|
THP1-defNLRP3 Cells NLRP3 Knockdown in THP-1 cells (human monocytes) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-dnlp
|
|
||
|
THP1-defNLRP3 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-dnlp-av
|
Notification: Reference #thp-konlrp3z-av can only be ordered together with reference #thp-konlrp3z.
Reference #thp-dnlp-av can only be ordered together with reference #thp-dnlp.
NLRP3 knockout or knockdown in THP-1 cells
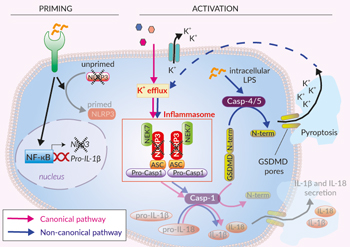
Canonical and non-canonical activation of NLRP3
NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3, cryopyrin or NALP3) is a cytoplasmic protein and the best-described inflammasome sensor [1, 2]. The inflammasome response requires two signals, priming (recognition of PAMPs or DAMPs by pattern recognition receptors such as TLRs) and activation. Activation of NLRP3 can be induced by a wide range of stimuli (e.g. Nigericin, ATP, crystals), and instead of directly binding to them, NLRP3 senses downstream cytosolic stress signals such as ion imbalances (i.e. K+ efflux).
To foster research on the NLRP3 sensor, InvivoGen provides cellular tools that have been generated from the human monocytic THP1 cell line through either a stable knockout or knockdown of the NLRP3 gene. THP-1 cells are widely used for inflammasome studies due to their high expression levels of NLRP3, ASC, and pro-caspase-1.
• THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells – Knockout (KO) of the N-terminal region of the NLRP3 gene
• THP1-defNLRP3 cells – Knockdown (KD) of the NLRP3 gene
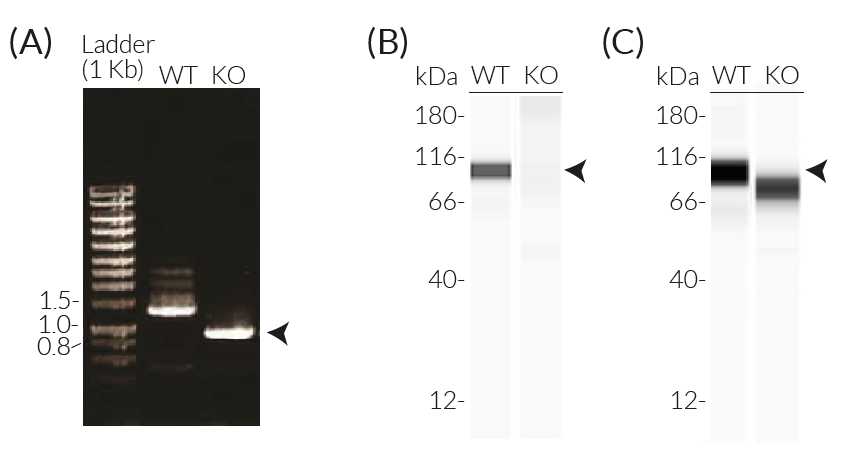
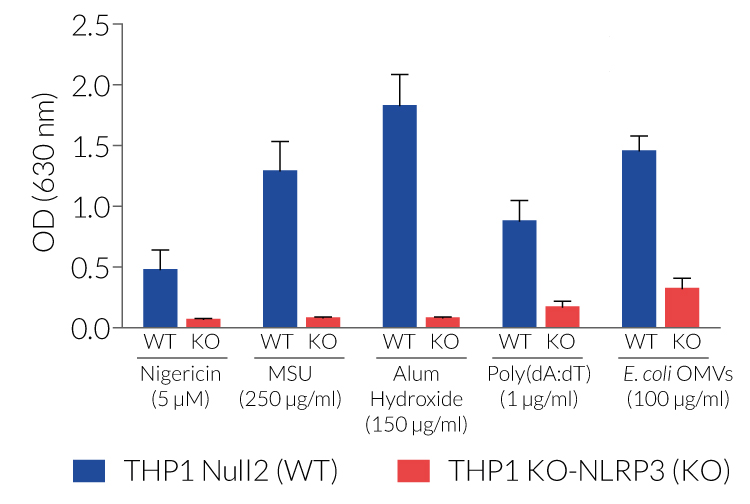
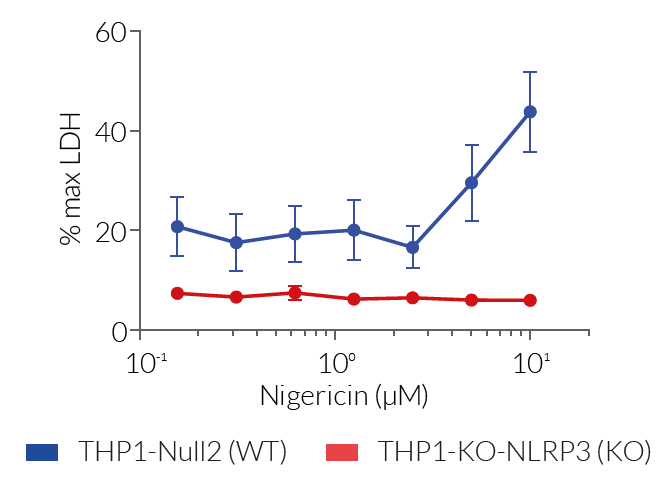
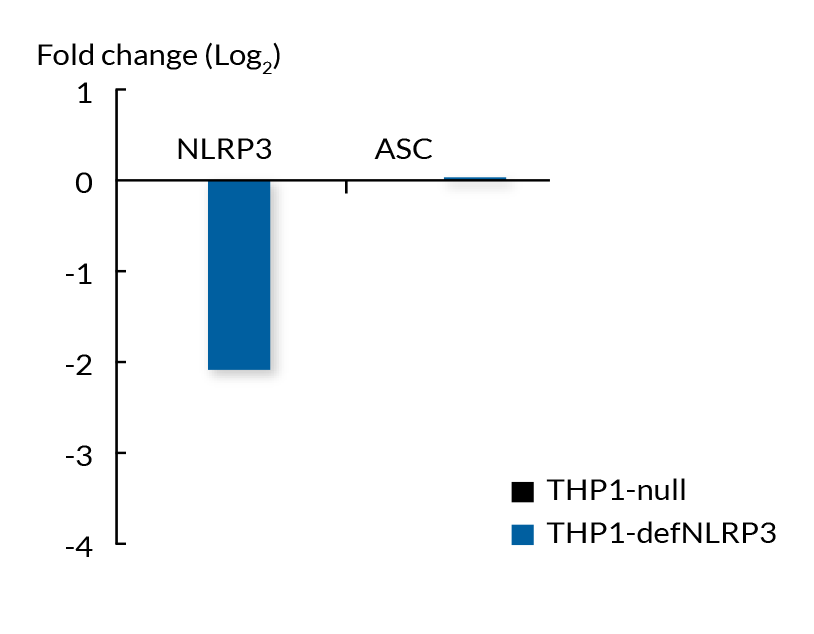
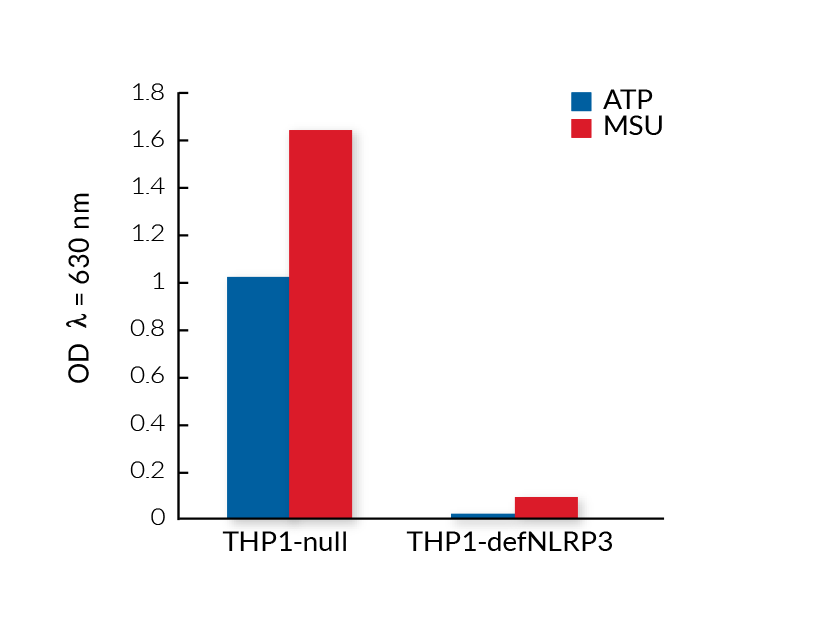
These cell lines exhibit a similar phenotype but have dramatically different genotypes. They share the common phenotype of abrogation of mature IL-1β secretion. However, THP1- defNLRP3 cells exhibit a knockdown of NLRP3 gene expression whereas THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells possess a KO of the N-terminal region of the NLRP3 gene. Indeed, THP1- defNLRP3 cells have a maximum 2-fold reduction in NLRP3 expression, whereas THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells have no functional NLRP3 protein expression. These cell lines are useful tools in the study of the NLRP3 sensor in inflammasome responses and can also be used as control cell lines for the screening of novel therapeutics that target NLRP3 signaling pathways.
Features of THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells:
- Generated from the parental cell line THP1-Null2
- Verified biallelic KO of the N-terminal region of the NLRP3 gene (DNA sequencing, PCR, and Western blot)
- Complete abrogation of mature IL-1β secretion upon activation of NLRP3
- Differing pyroptotic cell death depending upon activation of NLRP3 by canonical or non-canonical inflammasomes
Features of THP1-defNLRP3 cells:
- Generated from the parental cell line THP1-Null
- Verified KD of the NLRP3 gene (RT-qPCR)
- Significantly reduced mature IL-1β secretion upon activation of the NLRP3
- Highly referenced in inflammasome-related literature (see citations)
For detecting and quantifying the release of mature human (h)IL-1β, InvivoGen provides HEK-Blue™ IL-1β sensor cells, which express an NF-κB-inducible SEAP reporter gene. QUANTI-Blue™ Solution allows rapid colorimetric detection and measure of SEAP activity by reading the optical density at 630-650 nm.
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
References:
1. Swanson K.V. et al., 2019. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19:477.
2. Groslambert M. & Py B. 2018. Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 11:359.
Specifications
THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Quality Control:
- Biallelic knockout of the N-terminal region of the NLRP3 gene has been verified by DNA sequencing, PCR, Western blot (WES™), and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
THP1-defNLRP3 cells
Antibiotic resistance: Hygromycin B
Growth Medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 μg/ml Normocin™
Quality control:
- NLRP3 deficiency (def) has been verified by qRT-PCR and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells
- 3-7 x 106 THP1-KO-NLRP3 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml). Store at 4 °C or at -20 °C.
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA & Canada)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA & Canada)
THP1-defNLRP3 cells
- 3-7 x 106 THP1-defNLRP3 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Hygromycin B Gold (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic multi-protein complexes that assemble in response to infections and cellular damage. Canonical and non-canonical inflammasomes have been identified. Canonical inflammasomes are characterized by a primary sensor, such as NLRP3, that recruits the ASC adaptor leading to caspase-1 (CASP1) activation.
The canonical inflammasome response requires two signals, priming (recognition of PAMPs or DAMPs by pattern recognition receptors such as TLRs) and activation [1,2]. Activation of NLRP3 can be triggered by a wide range of structurally and chemically unrelated stimuli (e.g. pore-forming toxins, activators of ion channels, MSU crystals, β-amyloid proteins). Therefore, instead of directly binding to these stimuli, NLRP3 senses downstream cytosolic stress signals such as ion imbalances (e.g. K+ efflux) [2]. This leads to the aggregation of NLRP3 and the ASC adaptor and the cleavage and activation of CASP1. This induces the maturation of pro-IL-1β/pro-IL-18, and cleavage of the pore-forming protein gasdermin D (GSDMD), leading to the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 as well as pyroptosis [1,2].
Additionally, NLRP3 is activated indirectly by the induction of the non-canonical inflammasome (CASP4/5 in humans and CASP11 in mice) upon the sensing of cytosolic LPS. These caspases trigger GSDMD‑driven release of alarmins and K+ efflux, which ultimately induces the activation of NLRP3 and CASP1-mediated IL-1β/-18 maturation and secretion [1,2].
1. Swanson K.V. et al., 2019. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19:477.
2. Groslambert M. & Py B. 2018. Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 11:359.