IL-17 Reporter HEK 293 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ IL-17 Cells Human IL-17 Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-il17
|
|
||
|
HEK-Blue™ IL-17 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-il17-av
|
Notification: Reference #hkb-il17-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-il17.
IL-17 Reporter Cells
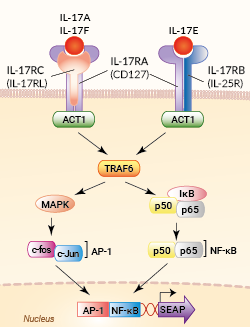
Signaling pathway in HEK-Blue™ IL-17 cells
HEK-Blue™ IL-17 cells were engineered from the human embryonic kidney HEK293 cell line to detect bioactive human interleukin 17A (IL-17A) and IL-17F, as well as human and murine IL-17E (also known as IL-25), by monitoring the activation of the NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. In addition, these cells can be used for screening antibodies or small molecule inhibitors targeting the IL-17 pathway.
IL-17 is a family of six closely related cytokines (IL-17A to IL-17F) which have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory activities [1, 2].
Cell line description
HEK-Blue™ IL-17 cells were generated by stable transfection with the genes encoding for the human IL-17 receptor (IL-17RA and IL-17RC chains), the ACT1 adaptor molecule, as well as an NF-κB- and AP-1-inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter. The binding of IL-17 to its receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to the activation of NF-κB/AP-1 and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
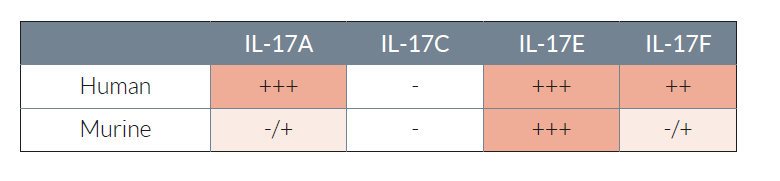
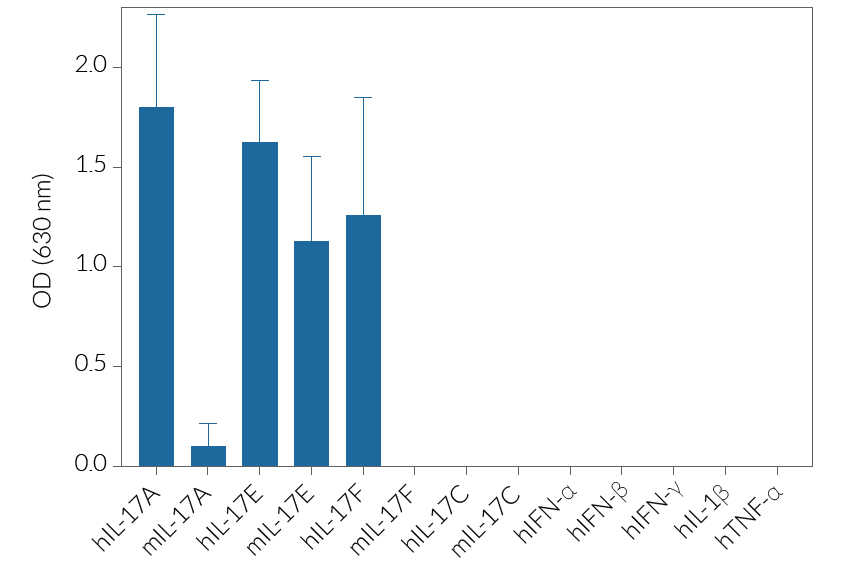
HEK-Blue™ IL-17 cells detect human (h) IL-17A, hIL-17E, hIL-17F, and murine (m) IL-17E. They display little to no response to mIL‑17A and mIL-17F. They do not respond to hIL-17C, mIL-17C. Of note, they are not responsive to hTNF-α and hIL-1β (see figures).
Key features
- Fully functional IL-17 signaling pathway
- Readily assessable NF-κB/AP-1-SEAP reporter activity
- Strong response to hIL-17A, hIL-17F, & h/m IL-17E
- Low to no response to mIL-17A, h/mIL-17C, & mIL-17F
- No response to hTNF-α and hIL-1β
Applications
- Detection and quantification of hIL-17A & hIL-17F activity
- Detection and quantification of h/mIL-17E (IL-25) activity
- Screening of anti-IL-17 or anti-IL-17 receptor antibodies
- Screening and release assay of small molecule inhibitors of the IL-17 pathway
References:
1. Monin L. & Gaffen S.L., 2018. Interleukin 17 family cytokines: signaling mechanisms, biological activities, and therapeutic implications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 10(4).
2. Pappu R. et al., 2011. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology. 134: 8-16.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Hygromycin, Zeocin®
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2-4 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 100 μg/ml Normocin®
Specificity: human IL-17A, human IL-17F, and human & mouse IL-17E (IL-25)
Detection range:
- human IL-17A: 1- 100 ng/ml
- human & mouse IL-17E (IL-25): 1- 100 ng/ml
- human IL-17F: 3 - 100 ng/ml
Quality Control:
- SEAP reporter activity in response to IL-17 is validated using functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages following thawing is confirmed.
- These cells are tested for mycoplasma contamination.
Contents
- 1 vial containing of 3-7 x 106 cells
- 2 x 1 ml HEK-Blue Selection (250X concentrate)
- 1 ml Normocin® (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
Interleukin 17 (IL-17) is a family of six closely related cytokines (IL-17A to IL-17F) which have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory activities. IL-17A and IL-17F, which can form a heterodimer, play an important role in Th17 immunity and are implicated in tumorigenesis and autoimmune diseases, whereas IL-17E (also known as IL-25) appears to promote Th2 immunity [1,2].
IL-17 cytokines exert their biological activities by binding to heterodimeric receptors containing the ubiquitous IL-17RA chain and a second IL-17R(C, B or E) chain. IL-17A and IL-17F bind to the IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptor, IL-17C binds to the IL-17RA/IL-17RE receptor, and IL-17E binds to the IL-17RA/IL-17RB receptor [1, 2]. The activated heterodimeric receptor recruits the Act1 adaptor and induces the TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) ubiquitylation. This triggers a signaling cascade that results in NF-κB and AP-1 activation [1].
1. Monin L. & Gaffen S.L., 2018. Interleukin 17 family cytokines: signaling mechanisms, biological activities, and therapeutic implications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 10(4).
2. Pappu R. et al., 2011. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology. 134: 8-16.