TL1A reporter cell line
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ TL1A Cells Human & Mouse TL1A Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-tl1a
|
|||
|
HEK-Blue™ TL1A vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-tl1a-av
|
![]() Cytokine offer: For each cytokine reporter cell line purchased, get a free vial of the matching cytokine.
Cytokine offer: For each cytokine reporter cell line purchased, get a free vial of the matching cytokine.
TL1A responsive NF-κB/AP1-SEAP reporter assay
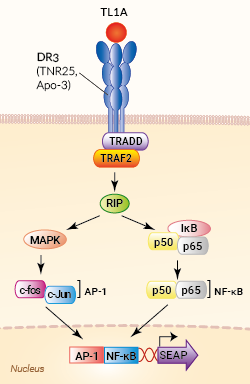
Signaling pathway in HEK-Blue™ TL1A cells
InvivoGen also offers:
HEK-Blue™ TL1A cells are designed to monitor human TL1A-induced NF-κB/AP1 stimulation or inhibition. This colorimetric cytokine bioassay can be used to screen activatory or inhibitory molecules, such as engineered cytokines and neutralizing antibodies, respectively.
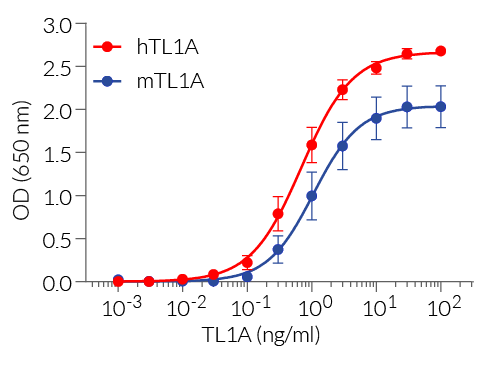
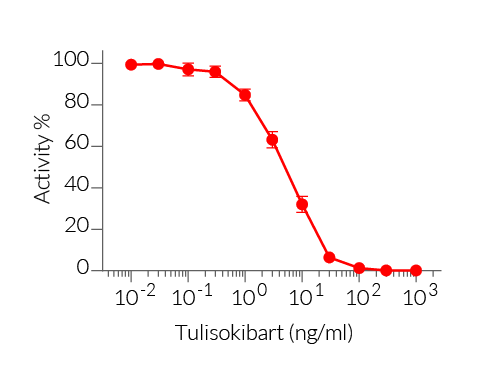
TL1A reporter cells respond specifically to recombinant mouse (m) and human (h)TL1A. Their reliable and consistent performance makes them suitable for release assays of activatory and inhibitory molecules such as Tulisokibart, a monoclonal antibody that targets TL1A and prevents its binding to its receptor (see figures).
Key features
- Readily assessable NF-κB/AP1 reporter activity
- Convenient readout using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution
- High sensitivity to human (h)TL1A and mouse (m)TL1A activity
- Stability guaranteed for 20 passages
Applications
- Therapeutic development
- Drug screening
- Release assay
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like 1A (TL1A) drives the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and differentiation of T helper subsets. Abnormal TL1A expression is linked to enteric autoimmune diseases (e.g. Crohn’s disease) and extends to other diseases, including allergic airway inflammation.
InvivoGen’s products are for internal research use only and not for clinical or veterinary use.
Back to the topSpecifications
Cell type: Epithelial
Tissue origin: Human Embryonic Kidney
Target: TL1A
Specificity: Human, Mouse
Reporter gene: SEAP
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Zeocin®
Detection range: 300 pg/ml - 30 ng/ml (hTL1A and mTL1A)
Growth medium: Complete DMEM (see TDS)
Growth properties: Adherent
Mycoplasma-free: Verified using Plasmotest™
Quality control: Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
Back to the topContents
HEK-Blue™ TL1A Cells (hkb-tl1a)
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Normocin® (50 mg/ml)
-
1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
HEK-Blue™ TL1A vial (hkb-tl1a-av)
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Notification: Reference #hkb-tl1a-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-tl1a.
Back to the topDetails
Cell line description
HEK-Blue™ TL1A cells were generated by stable transfection of the human embryonic kidney HEK293 cell line with the gene encoding the human Death Receptor 3 (DR3) and a SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) reporter gene under the control of the IFN-β minimal promoter fused to five AP-1 and five NF-κB binding sites.
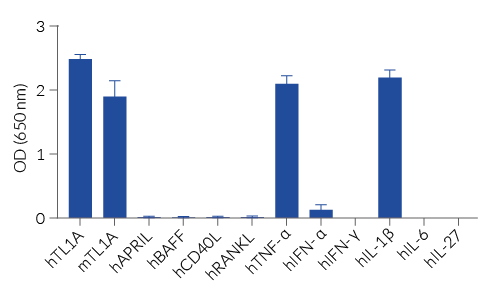
The binding of TL1A to its receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to AP-1/NF-κB activation and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent. HEK-Blue™ TL1A cells detect human (h) and mouse (m) TL1A. Of note, these cells also respond to two other human AP-1/ NF-κB-signaling cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1 β. However, they do not respond to other cytokines of the TNF superfamily: APRIL, BAFF, RANKL, and CD40L (see figures).
TL1A background
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like 1A (TL1A), also called TNFSF15, is a cytokine that belongs to the TNF superfamily. TL1A is produced by endothelial cells, activated dendritic cells, and macrophages. It is synthesized as a membrane-bound trimeric molecule. Alternative splicing or cleavage by the tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme results in soluble TL1A [1]. Both forms bind the homotrimeric transmembrane death receptor 3 (DR3), triggering TRADD/TRAF2/RIP signaling, and ultimately leading to NF-κB and MAPKs activation. Subsequent gene expression in target cells drives the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and differentiation of T helper subsets [1].
Relevance for therapeutics development
TL1A is normally responsible for mediating protective immune responses. However, it can also play a role in chronic inflammatory disorders and have harmful impacts. Abnormal TL1A expression or TL1A overactivity promotes excessive inflammation and immune cell infiltration, contributing to tissue damage and further inflammation amplification [1].
Pharmaceutical companies have developed potent monoclonal antibodies to block TL1A signaling and stop the downstream inflammatory cascade and tissue damage, primarily in the onset of asthma and Crohn’s disease. Anti-TL1A inhibitors such as Tulisokibart (MK-7240 or PRA023, Merck), RVT-3101 (PF-06480605, Roche), and Duvakitug (TEV-48574, Sanofi & Teva Pharmaceuticals) have demonstrated "best-in-class" potential for treating inflammation and scarring in IBD [2-4]. Duvakitug is currently being studied for its safety as an asthma medication [5-6].
References:
1. Xu W.D., et al., 2022. Role of TL1A in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Immunol. 13: 891328.
2. Sands, B.E., et al., 2024. Phase 2 Trial of Anti-TL1A Monoclonal Antibody Tulisokibart for Ulcerative Colitis. N Engl J Med, 391(12): p. 1119-1129.
3. Danese, S., et al., 2021. Anti-TL1A Antibody PF-06480605 Safety and Efficacy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Phase 2a Single-Arm Study. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 19(11): p. 2324-2332.e6.
4. Solitano, V., et al., 2024. TL1A inhibition for inflammatory bowel disease treatment: From inflammation to fibrosis. Med. 5(5): p. 386-400.
5. Balyan, R., et al.,, 2024. P633 First-in-Human Pharmacokinetic and Safety Study of an Anti-TL1A Antibody, TEV-48574, in Healthy Volunteers and Asthma Patients. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 18(Supplement_1): p. i1215-i1216.
6. Raphael, G., et al., 2024. P1061 TEV-48574, an anti-TL1A antibody in development for use in IBD, is safe and well tolerated following 16 weeks of subcutaneous treatment in adults with severe uncontrolled T2-low/non T2 asthma. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 18(Supplement_1): p. i1908-i1908.