IL-18 Reporter HEK 293 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 Cells Human & Mouse IL-18 Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-hmil18
|
|||
|
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
hkb-hmil18-av
|
![]() Cytokine offer: For each cytokine reporter cell line purchased, get a free vial of the matching cytokine.
Cytokine offer: For each cytokine reporter cell line purchased, get a free vial of the matching cytokine.
IL-18 Reporter Cells
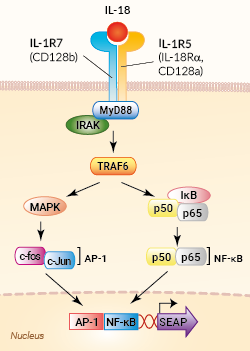
Signaling pathway in HEK-Blue™ IL-18 cells
InvivoGen also offers:
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 cells were engineered from the human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cell line to detect bioactive interleukin-18 (IL-18) by monitoring the activation of the NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. These cells are useful to monitor IL-18 secretion in inflammasome activation studies. In addition, these cells can be used for screening antibodies or small molecule inhibitors targeting the IL-18 pathway.
IL-18 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that causes a wide variety of biological effects associated with infection, inflammation, and autoimmune processes [1, 2].
Cell line description
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 cells were generated by stable transfection with the genes encoding the IL-18 receptor (IL-18R) and IL-18 receptor accessory protein (IL-18RAP). These cells were further transfected with an NF-κB/AP-1-inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter. The binding of IL-18 to its heterodimeric IL-18 receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to NF-κB/AP-1 activation and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
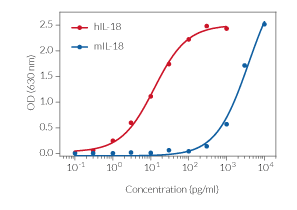
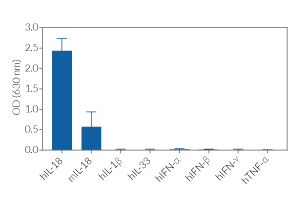
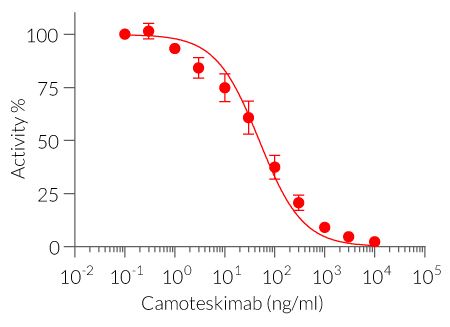
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 cells are highly sensitive to human (h) IL-18 and also respond to a lesser extent to murine (m) IL-18. They can also be used for screening and release assay of molecules that inhibit IL-18 signaling, such as Camoteskimab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-18 (see figures). These cells are non‑responsive to hIL-1β, hIL-33, hIFN-α, hIFN-β , hIFN-γ, and hTNF-α (see figures).
Key Features
- Fully functional IL-18 signaling pathway
- Readily assessable NF-κB/AP-1-inducible SEAP reporter activity
- Strong response to human (h) IL-18 and lower response to murine (m) IL-18
- No response to hTNF-α and hIL-1β
Applications
- Detection and quantification of hIL-18 and mIL-18 activity
- Screening of anti-IL-18 and anti-IL-18 receptor antibodies
- Screening of small molecule inhibitors of the IL-18 pathway
References:
1. Yasuda K. et al., 2019. Interleukin-18 in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3).
2. Dinarello CA. et al., 1998. Overview of interleukin-18: more than an interferon-gamma inducing factor. J Leukoc Biol. 63(6):658-64.
3. Gracie JA. et al., 2003. Interleukin-18. J Leukoc Biol.3(2):213-24.
4. Kojima H. et al., 1998. Interleukin-18 activates the IRAK-TRAF6 pathway in mouse EL-4 cells. BBRC 244(1):183-6.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin, Hygromycin B, Zeocin®
Growth medium: DMEM, 4.5 g/l glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 100 μg/ml Normocin®
Specificity: Detects human and mouse IL-18
Detection range:
- hIL-18: 10 pg - 1 ng/ml
- mIL-18: 3 ng - 100 ng/ml
Quality Control:
- SEAP reporter activity in response to IL-18 is validated using functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages following thawing is confirmed.
- These cells are tested for mycoplasma contamination.
Contents
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 Cells (hkb-hmil18)
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
- 2 x 1 ml of HEK-Blue™ Selection (250x concentrate)
- 1 ml of Normocin® (50 mg/ml)
-
1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
HEK-Blue™ IL-18 vial (hkb-hmil18-av)
- 1 vial containing 3-7 x 106 cells
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Notification: Reference #hkb-hmil18-av can only be ordered together with reference #hkb-hmil18.
Back to the topDetails
Interleukin-18 (IL-18), formerly called interferon-γ (IFN-γ) inducing factor, is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that causes a wide variety of biological effects associated with infection, inflammation, and autoimmune processes [1, 2]. More specifically, IL-18 induces IFN-γ production and contributes to T-helper 1 (Th1) cell polarization.
IL-18 is produced by macrophages and other cells, as a pro-protein which is proteolytically processed to its active form by caspase 1, an enzyme that is activated within the inflammasome multiprotein complex. It binds to a heterodimeric receptor consisting of IL-18R and IL-18 receptor accessory protein (IL-18RAP). Upon binding, IL-18 activates NF-κB and AP-1 via signaling pathways that involve TRAF-6 [3, 4].
1. Yasuda K. et al., 2019. Interleukin-18 in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3).
2. Dinarello CA. et al., 1998. Overview of interleukin-18: more than an interferon-gamma inducing factor. J Leukoc Biol. 63(6):658-64.
3. Gracie JA. et al., 2003. Interleukin-18. J Leukoc Biol.3(2):213-24.
4. Kojima H. et al., 1998. Interleukin-18 activates the IRAK-TRAF6 pathway in mouse EL-4 cells. BBRC 244(1):183-6.