IRF5 KO Dual Reporter THP-1 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-IRF5 Cells IRF5 knockout NF-κB-SEAP and IRF-Lucia Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-koirf5
|
|
||
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-IRF5 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-koirf5-av
|
Notification: Reference #thpd-koirf5-av can only be ordered together with reference #thpd-koirf5.
IRF5 knockout dual reporter monocytes
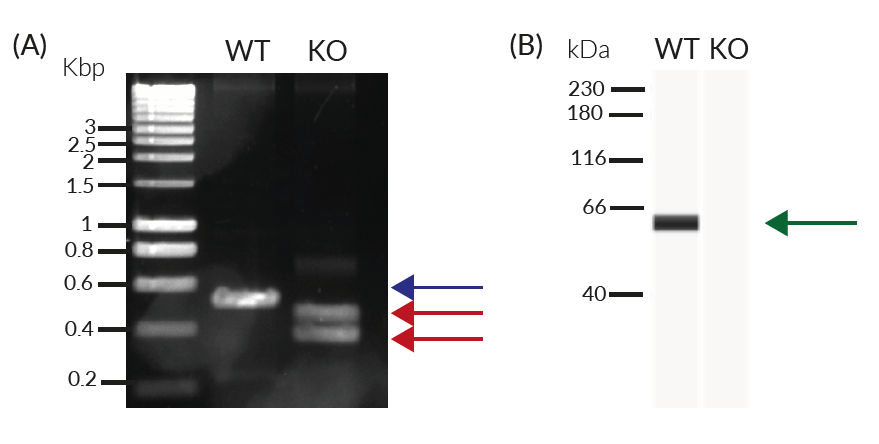
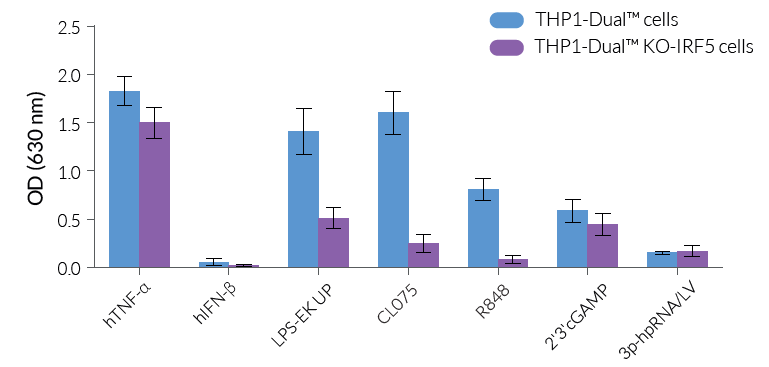
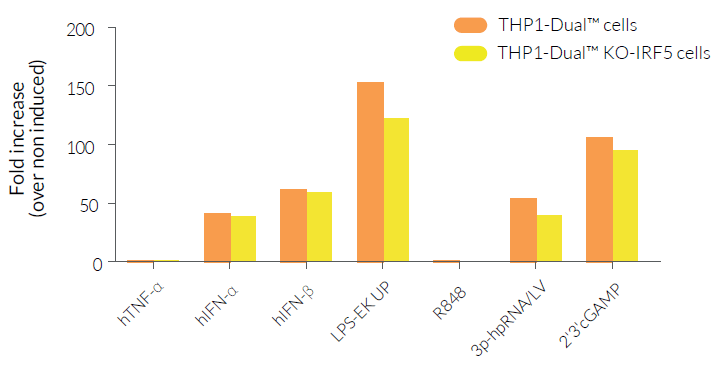
THP1-Dual™ KO-IRF5 cells were generated from the THP1-Dual™ cell line through the stable knockout of the IRF5 gene. They feature two inducible reporter genes, allowing the concomitant study of the IRF and NF-κB pathways, by monitoring the Lucia luciferase and SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) activities, respectively. As expected, NF-κB-mediated responses are significantly reduced in THP1-Dual™ KO-IRF5 cells upon incubation with TLR4 and TLR7/8 agonists [1] when compared to THP1-Dual™ cells, with no notable difference for the other ligands tested (see Figures).
Interferon regulatory receptor 5 (IRF5) is a transcription factor that plays a central role in inflammation, mediating the induction of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines [1]. IRF5 has been implicated downstream of several pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) [2]. There is increasing evidence that IRF5 plays a key role in numerous inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and inflammatory bowel disease [1,3]. Importantly, because IRF5 acts in a cell-type and activity-specific manner, it is an attractive therapeutic target [1].
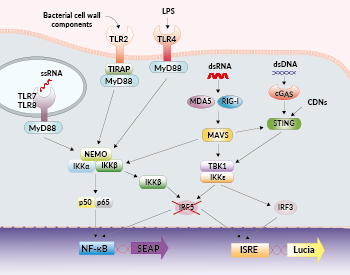
NF-κB and IRF signaling pathways in THP1-Dual™ KO-IRF5 cells
Key Features:
- Verified knockout of the IRF5 gene (PCR, DNA sequencing, and Western blot)
- Functionally validated with a selection of PRR ligands and cytokines
- Readily assessable Lucia luciferase and SEAP reporter activities
Applications:
- Defining the role of IRF5 in PRR-induced signaling, or other cell signaling pathways
- Highlighting the possible overlap between IRF5 and other signaling pathways
- Developing novel IRF5-targeting therapeutics
References
1. Almuttaqi, H. & Udalova, I.A. 2019. Advances and challenges in targeting IRF5, a key regulator of inflammation. FEBS J 286, 1624-1637.
2. Zhao, G.N. et al. 2015. Interferon regulatory factors: at the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1852(2):365-78.
3. Kaur, A. et al. 2018. IRF5-mediated immune responses and its implications in immunological disorders. Int Rev Immunol 37, 229-248.
Specifications
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin and Zeocin®
Quality Control:
- Biallelic IRF5 knockout has been verified by PCR, DNA sequencing, Western blot, and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 THP1-Dual™ KO-IRF5 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Details
IRF5 background
Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) is a transcription factor that plays a central role in inflammation. It mediates the induction of type I interferons (IFNs) and proinflammatory cytokines through binding to ISRE and NF-κB motifs, respectively [1]. IRF5 has been implicated downstream of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) [2]. Depending on the PRR that is triggered, IRF5 is activated through distinct mechanisms. TLR stimulation elicits IRF5 activation downstream of the MyD88 or the TRIF adaptors. Nucleic acid sensing by RIG-I, MDA5, cGAS or STING, elicits IRF5 activation through TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1). IRF5 can also be activated by the IKKβ kinase downstream of the MAVS adaptor associated with RIG-I or MDA5 [2]. IRF5 plays a key role in numerous inflammatory and autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and inflammatory bowel disease [1, 3]. Importantly, because IRF5 acts in a cell-type and activity-specific manner, it is an attractive therapeutic target [1].
1. Almuttaqi, H. & Udalova, I.A. 2019. Advances and challenges in targeting IRF5, a key regulator of inflammation. FEBS J 286, 1624-1637.
2. Zhao, G.N. et al. 2015. Interferon regulatory factors: at the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1852(2):365-78.
3. Kaur, A. et al. 2018. IRF5-mediated immune responses and its implications in immunological disorders. Int Rev Immunol 37, 229-248.