NLRC4 KO THP-1 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-KO-NLRC4 Cells NLRC4 Knockout in THP-1 cells (human monocytes) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-konlrc4z
|
|
||
|
THP1-KO-NLRC4 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-konlrc4z-av
|
Notification: Reference #thp-konlrc4z-av can only be ordered together with reference #thp-konlrc4z.
NLRC4 knockout in THP-1 cells
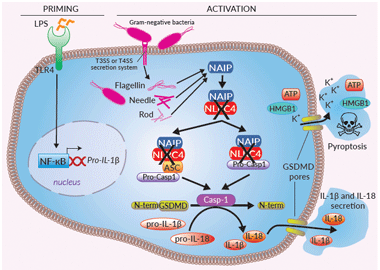
Inflammasome signaling in THP1-KO-NLRC4 cells
NLRC4 (Nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) and leucin-rich repeat (LRR) receptor, CARD domain-containing protein 4, or IPAF) is a cytoplasmic protein which upon activation, triggers the assembly of an NLRC4 inflammasome [1-3].
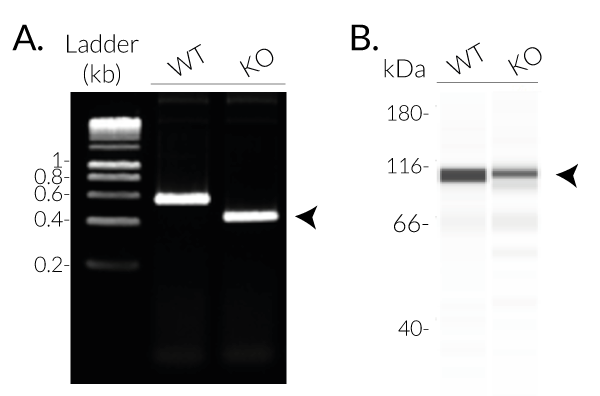
InvivoGen has developed THP1-KO-NLRC4 cells, a human monocytic cell line derived from THP1-Null2 cells through the deletion of the critical NBD region in the NLRC4 gene. NBD is essential for the NLRC4 polymerization and inflammasome assembly [1]. Thus THP1-KO-NLRC4 cells feature an inactive NLRC4 protein, unable to form a functional inflammasome.
• THP1-KO-NLRC4 cells – Knockout (KO) of the Nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) region of the NLRC4 gene
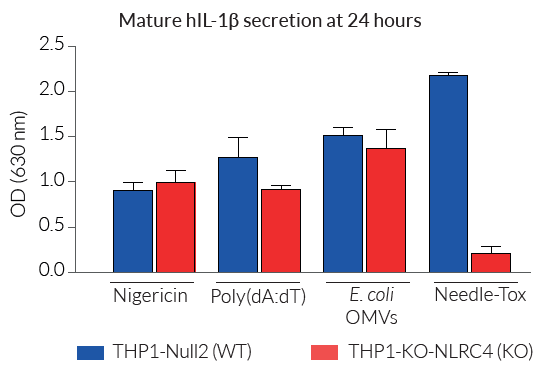
These cells exhibit impaired IL-1β secretion and pyroptosis upon incubation with known inducers of the NLRC4 inflammasome. Importantly, IL-1β secretion and pyroptosis remain unaffected upon incubation with other inflammasome inducers such as Nigericin (NLRP3 inducer).
Features of THP1-KO-NLRC4 cells:
- Absence of functional NLRC4 protein expression
- Verified biallelic knockout of the NOD region in the NLRC4 gene (DNA sequencing, PCR, and Western blot)
- Altered IL-1β secretion and pyroptosis early upon NLRC4 inflammasome activation
For the detection and quantification of mature human (h)IL-1β release, InvivoGen provides HEK-Blue™ IL-1β sensor cells, which express an NF-κB-inducible SEAP reporter gene. QUANTI-Blue™ Solution allows rapid colorimetric detection and measure of SEAP activity by reading the optical density at 630-650 nm.
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
References:
1. Zhang L. et al., 2015. Cryo-EM structure of the activated NAIP2-NLRC4 inflammasome reveals nucleated polymerization. Science. 350:404-409.
2. Zhao Y. et al., 2011. The NLRC4 inflammasome receptors for bacterial flagellin and type III secretion apparatus. Nature. 477: 596-600.
3. Bauer R. & Rauch I., 2011. The NAIP/NLRC4 inflammasome in infection and pathology. Mol. Aspects Med. 2020 Jun 1:100863.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Quality Control:
- Biallelic knockout of the NBD region of the NLRC4 gene has been verified by DNA sequencing, PCR, and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 THP1-KO-NLRC4 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml). Store at 4 °C or at -20 °C.
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic multi-protein complexes, characterized by a primary sensor, that assemble in response to infections and cellular damage. NLRC4 is an indirect sensor that must associate with NAIP (NLR family apoptosis inhibitory protein) to induce the assembly of an NLRC4 inflammasome. A single NAIP operates upstream of NLRC4 in humans and recognizes intracellular Flagellin, Needle, or Rod from several Gram-negative bacterial strains [1]. These ligands are sensed by NAIP upon bacterial invasion, or cytosolic translocation through the bacterial type III or IV secretion systems (T3SS or T4SS).
Once recruited by NAIP, NLRC4 triggers a homo-polymerization through NBD-NBD interactions, allowing a CARD clustering [1]. The NLRC4 polymer further associates to pro-caspase-1, either through direct CARD-CARD interaction or through the binding of the ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein) adaptor [1]. Activation of caspase-1 induces the maturation of pro-IL-1β/pro-IL-18, cleavage of the pore-forming gasdermin D (GSDMD), secretion of IL-1β/-18, and pyroptosis [1-3]. The NLRC4 inflammasome appears to protect mucosal barriers such as the lung, stomach, and intestine from invading bacteria [3]. Gain-of-function mutations have been described in human NLRC4 and are associated with auto-inflammatory conditions [3].
1. Zhang L. et al., 2015. Cryo-EM structure of the activated NAIP2-NLRC4 inflammasome reveals nucleated polymerization. Science. 350:404-409.
2. Zhao Y. et al., 2011. The NLRC4 inflammasome receptors for bacterial flagellin and type III secretion apparatus. Nature. 477: 596-600.
3. Bauer R. & Rauch I., 2011. The NAIP/NLRC4 inflammasome in infection and pathology. Mol. Aspects Med. 2020 Jun 1:100863.