THP1-Dual™ KO-MAVS Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-MAVS Cells Human THP-1 Monocytes - MAVS knockout NF-κB-SEAP and IRF-Lucia Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-komavs
|
|
||
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-MAVS vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-komavs-av
|
Notification: Reference #thpd-komavs-av can only be ordered together with reference #thpd-komavs.
KO-MAVS dual reporter monocytes for RLR pathway studies
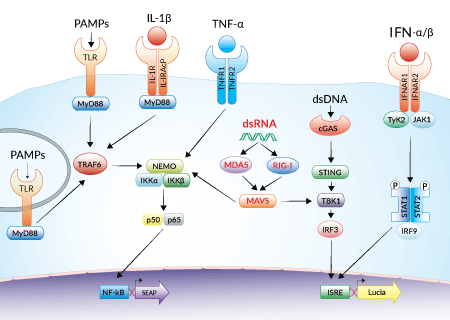
Reporter systems in THP1-Dual™-derived cells
InvivoGen offers a new series of THP1-Dual™ cell lines, derived from the human THP-1 monocytic cell line, and specifically designed for assessing the role of RIG-I, MDA5, and MAVS in the cytosolic RNA sensing pathways.
THP1-Dual™ KO-MAVS cells express two inducible reporter genes, allowing the concomitant study of the IRF and NF-κB pathways, by monitoring the Lucia luciferase and SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) activities, respectively. In addition, these cells feature stable knockout of the MAVS (Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein) gene.
RIG-I and MDA5 are two distinct sensors of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), a replication intermediate for RNA viruses [1-3]. Upon recognition of dsRNA, RIG-I and MDA5 are recruited by the MAVS adaptor to the outer membrane of the mitochondria leading to the activation of several transcription factors, including interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and NF-κB [3].
KEY FEATURES:
- Verified knockout of MAVS genes (PCR, DNA sequencing, Western blot, and functional assays)
- Functionally validated with a selection of PRR ligands and cytokines
- Readily assessable Lucia luciferase and SEAP reporter activities
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified
- Guaranteed mycoplasma-free
APPLICATIONS:
- Defining the role of MAVS in cytosolic RNA sensing pathways
- Highlighting possible overlap between RIG-I, MDA5, MAVS, and STING signaling functions
- Developing novel specific inhibitors of the RLR signaling pathway
References
1. Gebhardt A. et al., 2017. Discrimination of Self and Non-Self Ribonucleic Acids. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research 37: 184-97.
2. Pichlmair A. et al., 2006. RIG-I mediated antiviral responses to single-stranded RNA bearing 5’-phosphates. Science 314:997-1001.
3. Kawai T. et al., 2005. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol. 6(10):981-988.
Specifications
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Antibiotic resistance: Blasticidin and Zeocin®
Quality Control:
- Biallelic MAVS knockout has been verified by PCR, DNA sequencing, and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada, and some areas in Asia)
Details
MAVS (mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein, also known as IPS‑1, CARDIF, VISA)
MAVS is an adaptor protein that plays a critical role in the immune response to viral infection. The innate immune system senses intracellular double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), a replication intermediate for RNA viruses, through two RNA helicases: retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-association gene 5 (MDA5). Upon recognition of dsRNA, RIG-I and MDA5 are recruited by MAVS to the outer membrane of the mitochondria leading to the activation of several transcription factors including interferon-regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), IRF7, and NF-κB. IRFs and NF-κB regulate the expression of type I interferons (IFNs) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, respectively [1, 2].
RIG-I (retinoic-acid-inducible protein 1, also known as Ddx58)
RIG-I is a cytoplasmic RNA helicase that is critical for host antiviral responses. It senses double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), a replication intermediate for RNA viruses, leading to the production of type I interferons (IFNs) [1]. RIG-I binds specifically to short dsRNAs that have blunt ends and a 5’-triphosphate (5’-ppp) moiety, facilitating discrimination between host and viral dsRNA [3].
MDA5 (melanoma-differentiation-associated gene 5, also known as Ifih1 or Helicard)
MDA5 is a cytoplasmic RNA helicase that plays an important role in antiviral response. It senses long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), a replication intermediate for RNA viruses, leading to the production of type I interferons (IFNs) [1]. MDA-5 and the related RNA helicase RIG-I recognize a complementary set of cytosolic viral dsRNA. Transfected Poly(I:C), a synthetic analog of viral dsRNA, is recognized by both MDA-5 and RIG-I.
1. Gebhardt A. et al., 2017. Discrimination of Self and Non-Self Ribonucleic Acids. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research 37: 184-97.
2. Kawai T. et al., 2005. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol. 6(10):981-988.
3. Pichlmair A. et al., 2006. RIG-I mediated antiviral responses to single-stranded RNA bearing 5’-phosphates. Science 314:997-1001.










