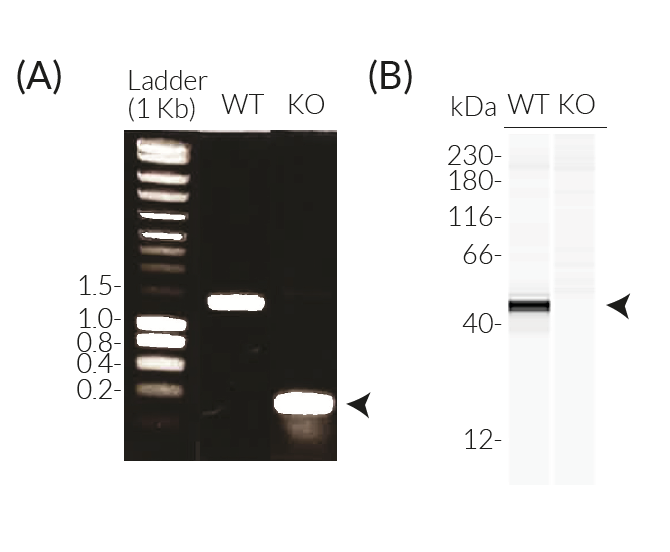
Caspase-4 KO THP-1 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-KO-CASP4 Cells CASP4 Knockout in THP-1 cells (human monocytes) |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-kocasp4z
|
|
||
|
THP1-KO-CASP4 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thp-kocasp4z-av
|
Notification: Reference #thp-kocasp4z-av can only be ordered together with reference #thp-kocasp4z.
Caspase-4 knockout in THP-1 cells
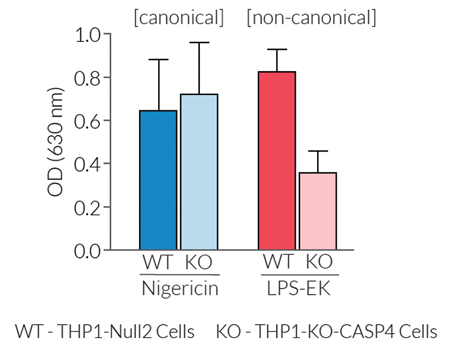
Inflammasome activation in THP1-KO-CASP4 cells
Human caspase-4 (CASP4) and CASP5, and their murine ortholog CASP11 are a family of inflammatory caspases that play a crucial role in the non-canonical inflammasome responses to intracellular lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [1-3].
InvivoGen has generated THP1-KO-CASP4 cells from the human monocytic THP1 cell line THP1-Null2 through the stable knockout of the caspase-4 (CASP4) gene.
• THP1-KO-CASP4 cells – Knockout (KO) of the CASP4 gene
In this cell line, mature IL-1β secretion is not affected when the canonical inflammasome is activated. However, mature IL-1β secretion is severely impaired upon activation of the non-canonical inflammasome by intracellular LPS. The remnant activity may be attributed to a partial rescue of the non-canonical inflammasome response by CASP5, a functional homolog of CASP4. THP1-KO-CASP4 cells are useful to study the role of CASP4 in inflammasome responses and to screen novel therapeutics that target the CASP4 signaling pathways.
Features of THP1-KO-CASP4 cells:
- Verified biallelic knockout of the CASP4 gene (both α and β isoforms) (DNA sequencing, PCR, and Western blot)
- Severe impairment of mature IL-1β secretion upon non-canonical inflammasome activation only
For detecting and quantifying the release of mature human (h)IL-1β, InvivoGen provides HEK-Blue™ IL-1β sensor cells, which express an NF-κB-inducible SEAP reporter gene. QUANTI-Blue™ Solution allows rapid colorimetric detection and measure of SEAP activity by reading the optical density at 630-650 nm.
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
References:
1. Schmid-Burgk J.L. et al., 2015. Caspase-4 mediates non-canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in human myeloid cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 45:2911.
2. Baker P.J. et al., 2015. NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of cytoplasmic LPS recognition by both caspase-4 and caspase-5. Eur. J. Immunol. 45:2918.
3. Lagrange B. et al., 2018. Human caspase-4 detects tetra-acylated LPS and cytosolic Francisella and functions differently from murine caspase-11. Nat. Commun. 9:242.
Specifications
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 µg/ml Normocin™
Quality Control:
- Biallelic CASP4 knockout has been verified by DNA sequencing, PCR, Western blot (Wes™), and functional assays.
- The stability for 20 passages, following thawing, has been verified.
- These cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 3-7 x 106 THP1-KO-CASP4 cells in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml). Store at 4 °C or at -20 °C.
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
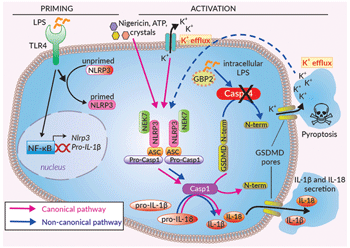
CASP4 is a 'non-canonical inflammasome' that senses intracellular lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Gram-negative bacteria and causes an inflammatory response, independent of TLR4 [1,2]. In the context of bacterial infection, LPS can be released from lysed bacteria as “free” LPS aggregates or actively delivered to the host cell through the release of small spherical bodies that encapsulate many bacterial components (i.e. toxins, DNA, RNA, and LPS) termed outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). Specifically, CASP4 binds to the Lipid A moiety of LPS, which features variable numbers of acylated fatty acid chains depending on the bacterial strain. Interestingly, CASP4 has a broader activity than its murine ortholog with it being able to bind both hexa-acylated (6 chains) as well as under-acylated (4-5 chains) lipid A [3]. Additionally, an IFN-inducible guanylate-binding protein GBP2 is an important co-factor required to trigger CASP4 activation in response to under-acylated LPS only [3]. CASP4 cannot cleave pro-IL-1β/-18, but instead triggers the cleavage of the pore-forming protein gasdermin D (GSDMD), leading to the release of alarmins and K+ efflux from the cell. This ultimately induces the activation of canonical inflammasome response, through NLRP3, and caspase-1-mediated IL-1β/-18 maturation and secretion [1,2].
1. Schmid-Burgk J.L. et al., 2015. Caspase-4 mediates non-canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in human myeloid cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 45:2911.
2. Baker P.J. et al., 2015. NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of cytoplasmic LPS recognition by both caspase-4 and caspase-5. Eur. J. Immunol. 45:2918.
3. Lagrange B. et al., 2018. Human caspase-4 detects tetra-acylated LPS and cytosolic Francisella and functions differently from murine caspase-11. Nat. Commun. 9:242.