THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 Cells
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 Cells Human THP-1 Monocytes - SAMHD1 knockout NF-κB-SEAP and IRF-Lucia Reporter Cells |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-kosamhd1
|
|
||
|
THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 vial Additional cell vial |
Show product |
3-7 x 10e6 cells |
thpd-kosamhd1-av
|
Notification: Reference #thpd-kosamhd1-av can only be ordered together with reference #thpd-kosamhd1.
SAMHD1 knockout NF-κB-SEAP and IRF-Lucia luciferase reporter monocytes
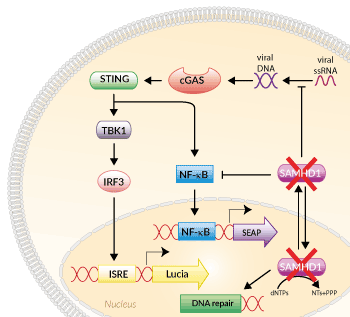
Signaling pathways in THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 Cells
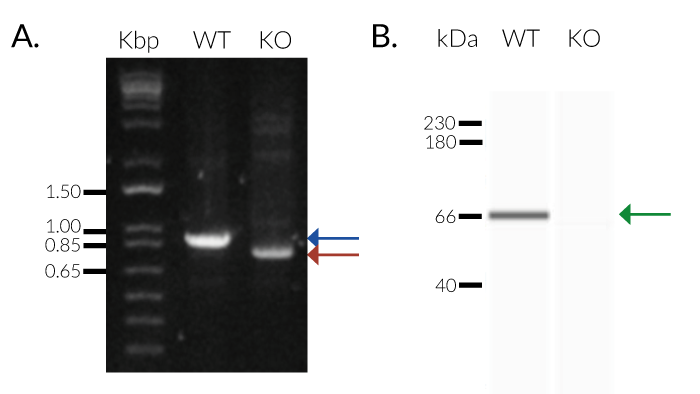
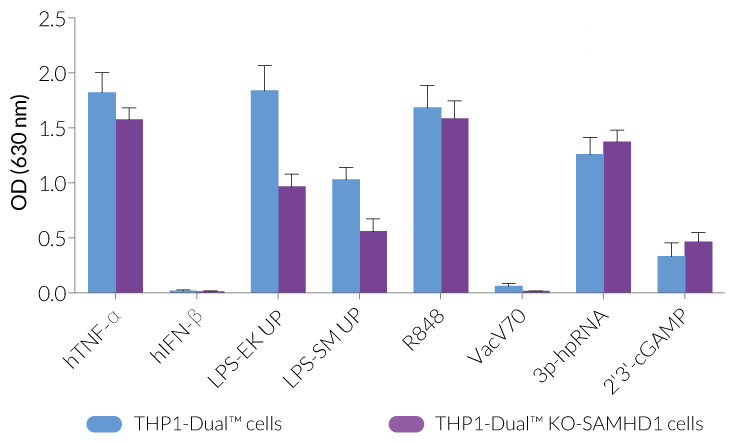
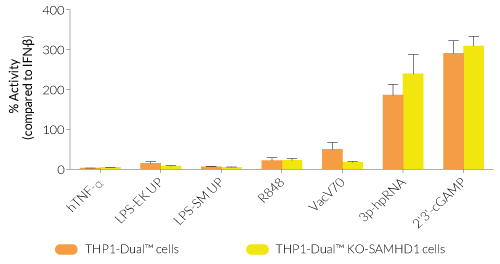
THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 cells were generated from THP1-Dual™ cells through the stable biallelic knockout of the SAMHD1 gene. Human THP1 monocytes or derived macrophages are a common cellular model to study DNA sensing as they naturally express all cytosolic DNA sensors identified so far (except DAI). THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 cells feature two inducible reporter genes, allowing the concomitant study of the IRF and NF-κB pathways, by monitoring the Lucia luciferase and SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) activities, respectively.
SAMHD1 (sterile alpha motif and histidine-aspartate domain-containing protein 1) is a predominantly nuclear enzyme playing a major role in nucleotide homeostasis by balancing cellular dNTP (deoxynucleoside triphosphate) levels [1]. Furthermore, it can influence viral activity and act as an important negative regulatory factor of the human innate immune response [1-3].
Key features:
- Biallelic knockout of the SAMHD1 gene
- Functionally validated with a selection of PRR ligands and cytokines
- Readily assessable Lucia luciferase and SEAP reporter activities
Applications:
- Study of IRF and NF-kB-dependent SAMHD1 signaling pathways
- Screening of interactions between SAMHD1 and other signaling protein
- Study the role of SAMHD1 in innate immunity, tumorigenesis, or viral replication
1. Deutschmann et al., 2021. SAMHD1 … and Viral Ways around It. Viruses. 2021;13(3):395.
2. Rice et al., 2009. Mutations involved in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome implicate SAMHD1 as a regulator of the innate immune response. Nature genetics, 41(7), 829–832.
3. Oo et al., 2022. Elimination of Aicardi–Goutières syndrome protein SAMHD1 activates cellular innate immunity and suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication. jbc.2022.101635
Specifications
Growth medium: RPMI 1640, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml Penicillin, 100 μg/ml Streptomycin, 100 μg/ml Normocin™
Antibiotic resistance: Zeocin®, Blasticidin
Quality control:
- Biallelic SAMHD1 gene knockout has been verified by PCR, western blot, DNA sequencing, and functional assays.
- The stability of this cell line for 20 passages following thawing has been verified.
- THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 cells are guaranteed mycoplasma-free.
Contents
- 1 vial of THP1-Dual™ KO-SAMHD1 cells (3-7 x 106 cells) in a cryovial or shipping flask
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml). Normocin™ is a formulation of three antibiotics active against mycoplasmas, bacteria, and fungi.
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
![]() Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Shipped on dry ice (Europe, USA, Canada and some areas in Asia)
Details
SAMHD1 plays a variety of roles in cell biology, immunology, and virology [1].
Using its phosphohydrolase activity, SAMHD1 converts dNTPs into inorganic triphosphates (PPPis) and deoxynucleosides (dN) to ensure efficient genome replication in dividing cells [2]. Moreover, it facilitates the replication fork progression and prevents DNA damage by actively recruiting members of the DSB (double-strand break) repair machinery [1].
Additionally, SAMHD1 can interfere with mediators of NF-κB and IRF signaling pathways, thus preventing an excessive antiviral and proinflammatory response [2]. Depending on whether a virus benefits from these suppressive effects on the host immune system, SAMHD1 allows for either antiviral or proviral events. SAMHD1 has been reported to limit HIV-1 replication while promoting Zika or SARS-CoV-2 infection [3].
Defects or alterations in the SAMHD1 gene have been associated with tumor development and Aicardi-Goutières syndrome, an autoimmune disorder characterized by spontaneous hyperactivation of the type I IFN pathway and excessive IFN-α production. This syndrome is also induced by mutations in other nuclease-coding genes such as TREX1 or RNASEH2 [3,4].
1. Coggins et al., 2020. SAMHD1 Functions and Human Diseases. Viruses, 12(4), 382.
2. Deutschmann et al., 2021. SAMHD1 … and Viral Ways around It. Viruses.13(3):395.
3. Oo et al., 2022. Elimination of Aicardi–Goutières syndrome protein SAMHD1 activates cellular innate immunity and suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication. jbc.2022.101635.
4. Rice et al., 2009. Mutations involved in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome implicate SAMHD1 as a regulator of the innate immune response. Nature genetics, 41(7), 829–832.